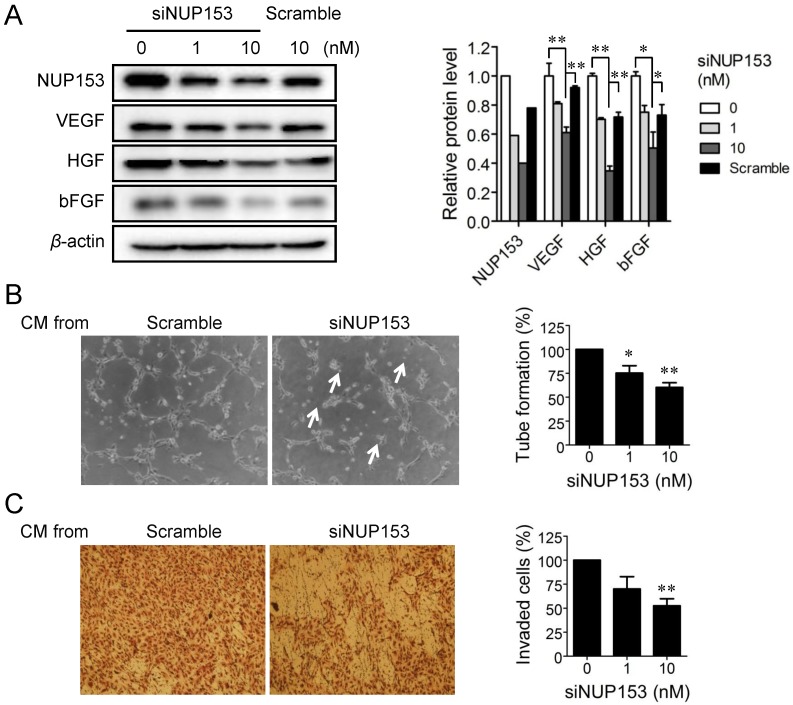
Figure 5.
The effect of nucleoporin 153 kDa knockdown via small interfering RNA on angiogenesis in cancer cells in vitro. (A) HeLa cells were treated with small interfering RNA against nucleoporin 153 kDa (siNUP153), and then the protein levels of nucleoporin 153 kDa (NUP153), vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF), and hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) were analyzed by Western blot. Scrambled small interfering RNA (Scramble) was used as the negative control. Quantitation of each protein level is shown in the bar graph. The level of β-actin protein expression was used for normalization; *p<0.05 and **p<0.01 between 0 vs 10 nM siNUP153 or 10 nM siNUP vs scrambled siRNA (Student's t-test). (B, C) Human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) were incubated with the conditioned media (CM) from HeLa cells treated with either siNUP153 or Scramble, and then tube formation (B) and invasion (C) assays were performed. HUVEC tube formation and invasion were quantified and plotted using Graphpad Prism (right panels). Arrows indicate broken tube networks following NUP153 knockdown. Data represent mean ± standard error from four independent experiments; *p<0.05 and **p<0.01 versus control (One sample t-test).