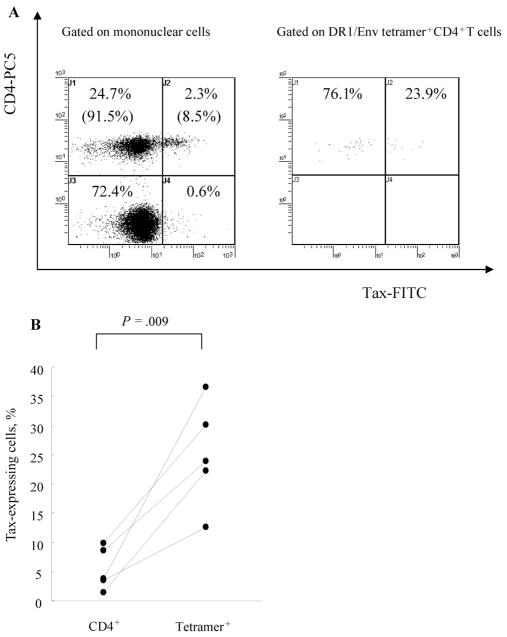
Figure 3.
Increased frequency of Tax expression in human T lymphotropic virus type 1 (HTLV-1) Env380 –399 –specific CD4+ T cells compared with that in total CD4+ T cells, in patients with HTLV-1–associated myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis (HAM/TSP). A, Intracellular detection of HTLV-1 Tax in DRB1*0101/Env380-394 (DR1/Env) tetramer+CD4+ T cells after 6 h of in vitro cultivation of peripheral blood mononuclear cells. One representative result from those for 5 patients with HAM/TSP is shown. The frequency of HTLV-1 Tax– expressing cells among DR1/Env tetramer+CD4+ T cells (23.9%) was higher than that of Tax-expressing cells among CD4+ T cells (8.5%). B, Data on all 5 patients with HAM/TSP tested. The frequency of HTLV-1 Tax– expressing cells among DR1/Env tetramer+CD4+ T cells was always higher than that of Tax-expressing cells among CD4+ T cells (for the no. of Tax+DR1/Env tetramer+CD4+ cells divided by total DR1/Env tetramer+CD4+ cells times 100, mean ± SD of 25.04% ± 8.99%; for the no. of Tax+CD4+ cells divided by total CD4+ cells times 100, mean ± SD of 5.34% ± 3.61%; P = .009, Mann-Whitney U test). Lines link 2 data points for each patient. At least 500 DR1/Env tetramer+CD4+ cells were analyzed for each sample. FITC, fluorescein isothiocyanate; PC5, cyanine 5–succinimidylester.