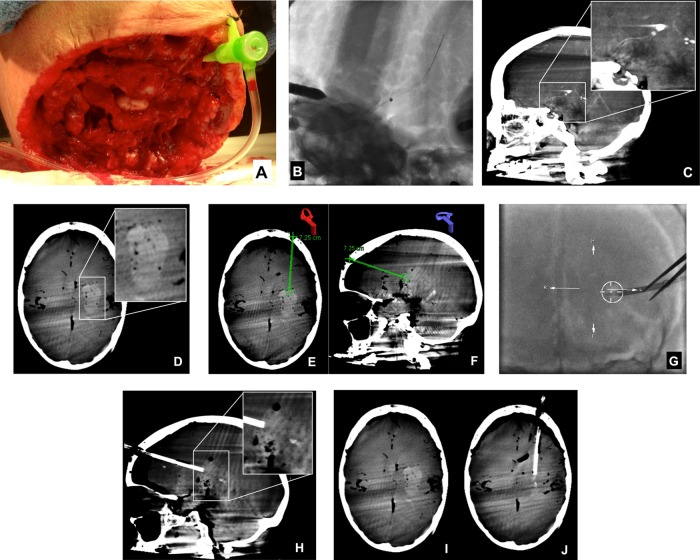
Figure 2.
Transvascular hematoma creation and CB-CT-guided hematoma evacuation with the Apollo system. A standard 6F sheath was inserted directly into the left internal carotid artery (A) and sutured into position. Next, a 5MAX catheter with an internal Hi Flo Renegade microcatheter was positioned at the left carotid terminus. After perforation of the carotid terminus with a microwire, the 5MAX catheter was manipulated over the Renegade microcatheter and microwire into the brain parenchyma (B). A sagittal reformation of cone beam CT data performed to document the position of the catheter tip (C), demonstrated its placement within the ipsilateral basal ganglia. After infusion of blood products through the 5MAX catheter and removal of the catheter, CB-CT confirmed the successful creation of a parenchymal hematoma (D). Using points demarcated on CB-CT and registered using the iGuide software (E and F), an 8F sheath was manipulated under live fluoroscopic guidance into the superficial aspect of the hematoma along its long axis. CB-CT was repeated to document the location of the sheath, demonstrating its position within the leading edge of the hematoma, in line with the long axis of the clot (H). These CB-CT data were then registered using the iGuide software, and the Apollo wand was introduced through the sheath freehand and activated to achieve clot evacuation under fluoroscopic guidance (see online supplementary movie 2). After clot evacuation, repeat CB-CT showed a marked reduction in the volume of hematoma with resolution of the local mass effect (I, J).