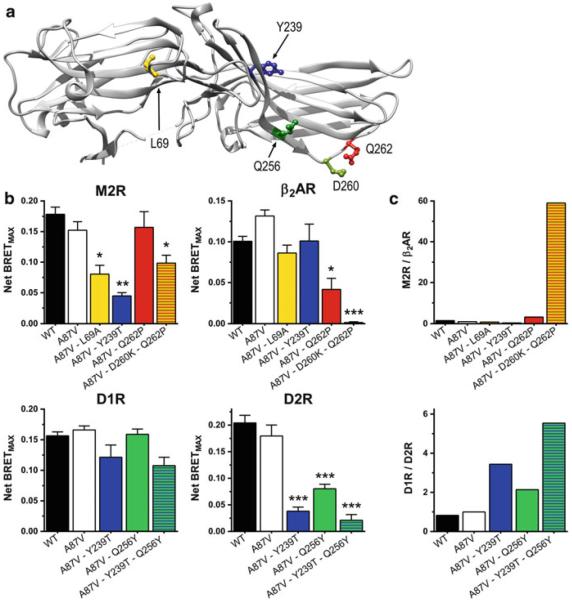
Fig. 2.
Mutations of few residues increase the selectivity of arr-3 for certain GPCRs. (a) The residues on the receptor-binding surface of bovine arr-3 that affected receptor selectivity the most (Gimenez et al. 2012b) are shown as ball-and-stick models. (b) The effect of these mutations and their combinations (on the Ala87Val background) on agonist-induced arr-3 recruitment (Net BRETmax) to M2 muscarinic (M2R), D1 (D1R) and D2 (D2R) dopamine, and β2-adrenergic (β2AR) receptors. (c) Ratios of net BRETMAX [shown in panel (b)] for the indicated mutants and receptor pairs are shown. For normalization, the binding ratio of the Ala87Val base mutant was set at 1. Asp260Lys + Gln256Tyr increased arr-3 preference for M2R over β2AR to >50-fold, whereas Tyr239Tre + Gln256Tyr increased arr-3 preference for D1R over D2R to approximately fivefold