Fig. 2.
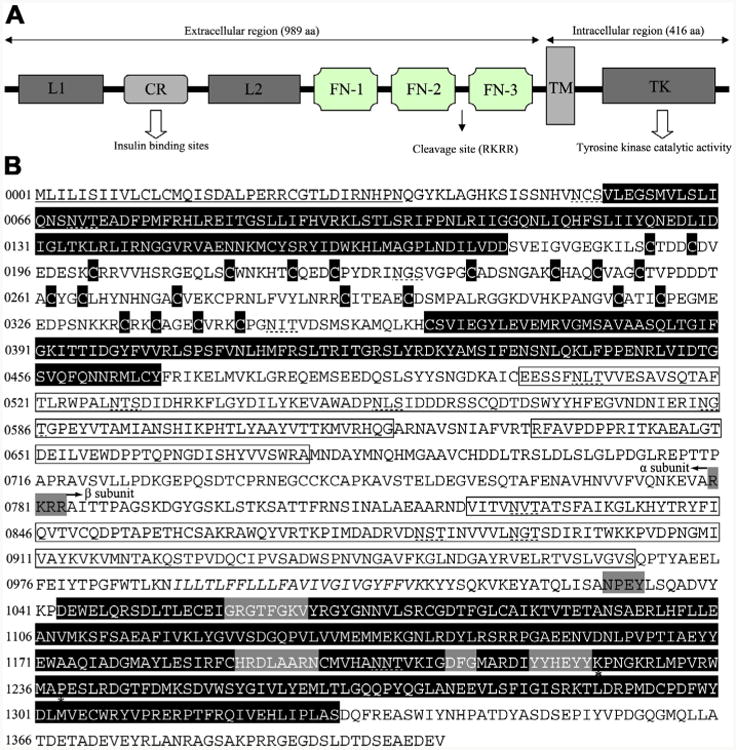
Insulin-like receptor of Haemonchus contortus consisting of representative structural domains. (A) Domain structure of the insulin-like receptor of Haemonchus contortus. Analysis of the amino acid sequence for the insulin-like receptor predicted all of the characteristic domains of insulin-like receptors from other taxa, including ligand binding loop 1 (L1) and loop 2 (L2); the cysteine-rich region (CR); three fibronectin type domains (FN-1, FN-2 and FN-3); the transmembrane domain (TM); and a tyrosine kinase domain (TK) (Konrad et al., 2003). (B) Protein sequence and structural features of the insulin-like receptor of H. contortus (Hc-DAF-2). The putative receptor L domains, cysteine residues of the CR domain and a TK domain are black boxes with white lettering, the FN domains are boxed. The TM region is italicised and conserved domains (GXGXXG, HRDLAARN, DFG and YXXXYY) (White et al., 1988) are boxed by a grey background. Further indicated are the potential proteolytic cleavage site RKRR (grey box) which divided the Hc-DAF-2 into a subunit and β subunit as well as the juxtamembrane NPxY and the Mg2+ binding domain. Two residues (K1224 and P1238) are marked by asterisks, which are highly conserved in the activation loop and might be involved in interaction with downstream signalling proteins (Hubbard, 1997; Massey et al., 2013). The signal peptide is underlined and the putative N-linked glycosylation sites (NxT/S) are marked with dashed lines.
