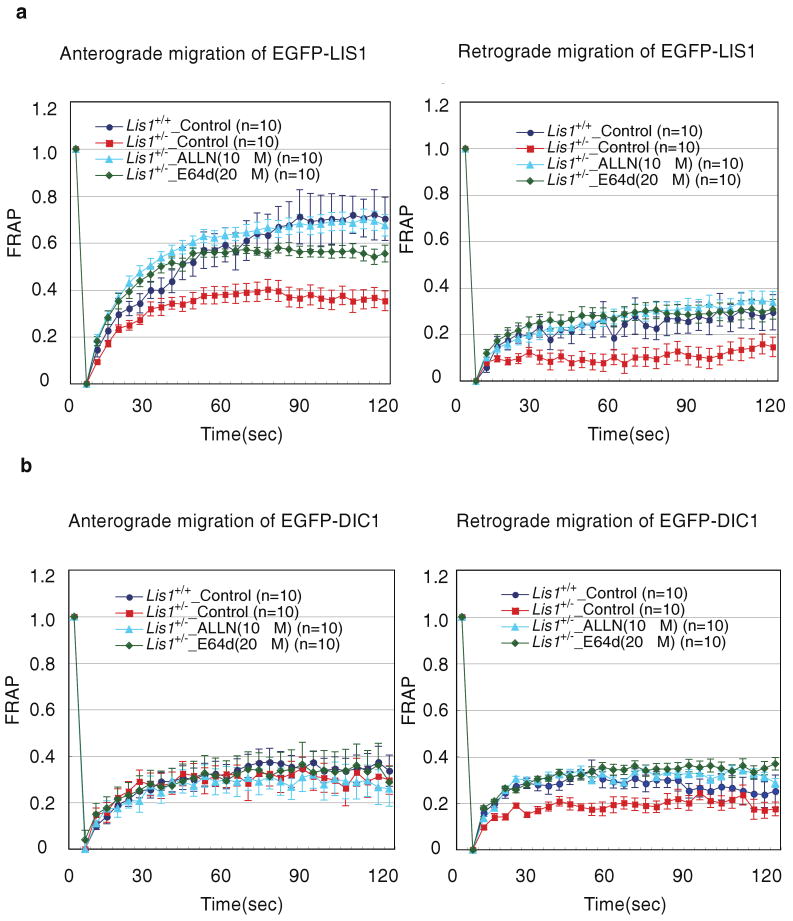
Figure 2. FRAP analysis of LIS1 or dynein intermediate chain1 (DIC1) transport after administration of ALLN or E64d using dorsal root gangalia (DRG) neurons.
We examined the effect of ALLN or E64d on LIS1 transport after two hours (a) using DRG neurons. Note: ALLN or E64d augments anterograde and retrograde transport of LIS1 in Lis1+/- DRG neurons to the wild type level. We also examined the effect of ALLN or E64d on DIC1 transport after two hours (b). Note: ALLN or E64d augments retrograde transport of DIC1 in Lis1+/- DRG neurons to the wild type level. DRGs from postnatal mice were dissociated using a previously described method (Lindsay, 1988). During dissociation of cells, D-MEM was used with 10% heat-inactivated bovine serum, 200 ng/ml 2.5s mNGF (Sigma) and 5 mM uridine/deoxfluorouridine (Sigma). The cells were plated onto poly-D-lysine coated dishes (MatTek) and cultured in the above medium for 48 hrs. DRGs were transfected with vectors to express EGFP-Lis1 or EGFP-DIC1 immediately after dissection using the Basic Nucleofector kit for primary neurons (Amaxa Biosystems). FRAP analyses were performed to extended axons from DRGs using the 510 META system (Carl Zeiss) 48 hours after transfection as described (Mochizuki, et al., 2001).