Figure 1.
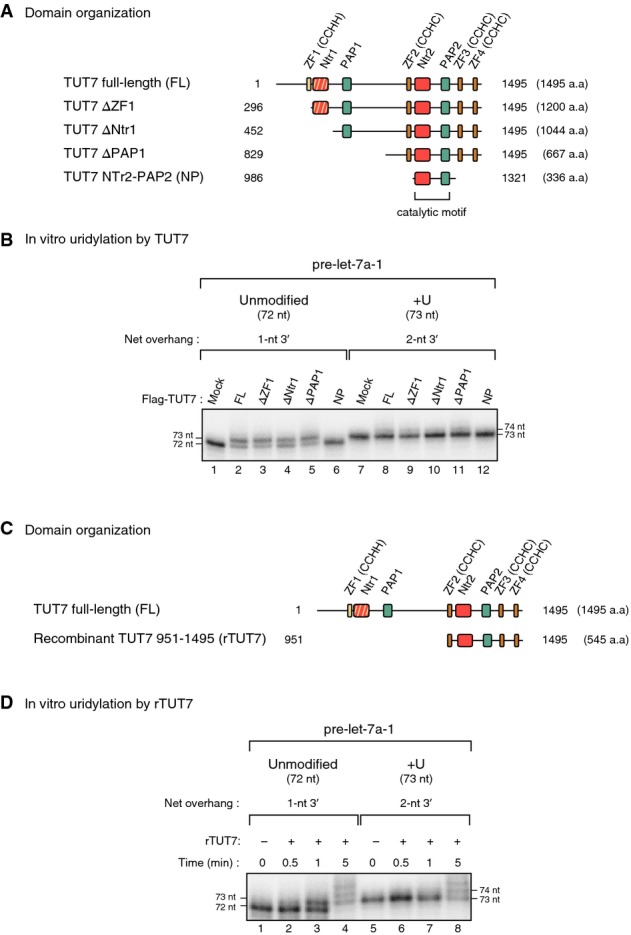
- Domain organization of full-length (FL) and deletion mutants (ΔZF1, ΔNtr1, ΔPAP1, and NP) of human TUT7. Yellow, CCHH-type zinc finger; hatched red, inactive nucleotidyl transferase domain due to a sequence variation; green, PAP-associated domain; orange, CCHC-type zinc finger; red, nucleotidyl transferase domain.
- In vitro uridylation of unmodified pre-let-7a-1 and mono-uridylated pre-let-7a-1 (+U) by immunopurified full-length TUT7 and deletion mutants (15 min reaction). Deletion mutants except for NP showed mono-uridylation activity and the same substrate preference as that of full-length TUT7; they mono-uridylate unmodified pre-let-7a-1 with a 1-nt 3′ overhang more efficiently than pre-let-7a-1 +U with a 2-nt 3′ overhang. NP mutant lost its uridylation activity.
- Domain organization of recombinant TUT7 951–1,495 (rTUT7).
- In vitro uridylation of unmodified pre-let-7a-1 and +U by rTUT7. rTUT7 exhibited mono-uridylation activity and the same substrate preference as full-length TUT7.
