Figure 2.
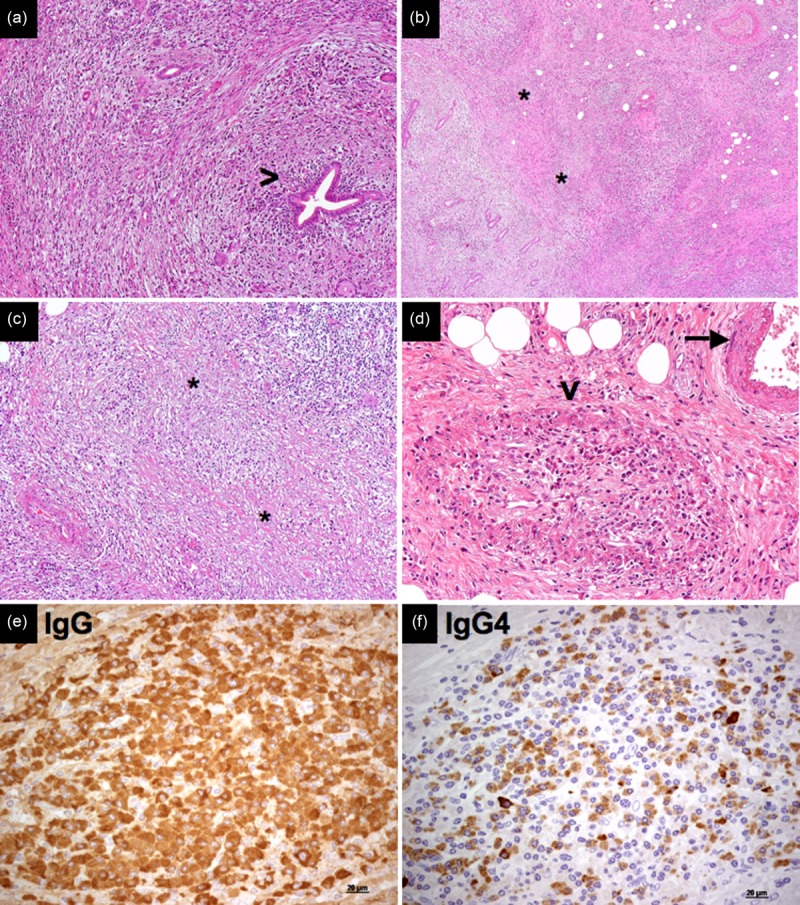
Pathological features of immunoglobulin (Ig)G4-related disease. (a) Pancreatic ducts are not affected by the fibroinflammatory infiltrate in IgG4-related autoimmune pancreatitis (arrowhead; haematoxylin and eosin, magnification ×100). (b,c) Areas of storiform fibrosis in IgG4-related autoimmune pancreatitis [asterisks; haematoxylin and eosin, magnification ×40 (b) and ×100 (c)]. (d) Obliterative phlebitis: an obliterated vein surrounded by an inflammatory nodule (arrowhead), next to an intact artery (arrow) (haematoxylin and eosin, magnification ×200). (e,f) Immunohistochemistry for IgG (e) and IgG4 (e) on sequential sections shows an IgG4/IgG ratio > 40% (magnification ×40).
