Figure 2.
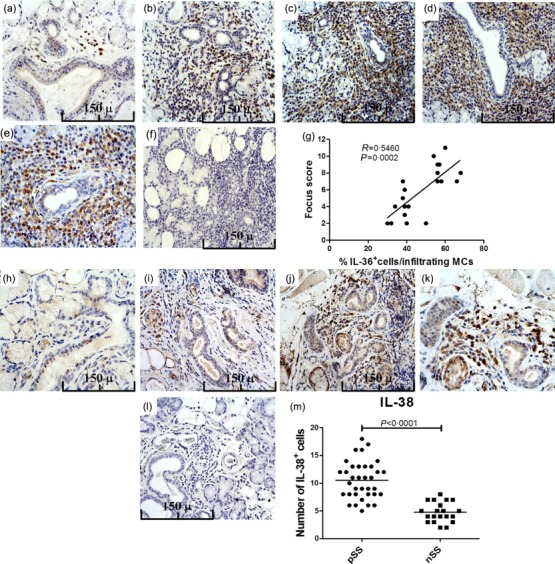
Interleukin (IL)-36α and IL-38 expression in primary Sjögren’s syndrome (pSS) patients’ minor salivary glands as assessed by immunohistochemistry. Representative microphotographs showing IL-36α immunostainings in 20 control subjects and 35 pSS patients. (a) IL-36α expression in minor salivary glands of controls. (b–e) IL-36α expression in the minor salivary glands of pSS patients with different focus score: focus scores 2 (b), 3 (c) and 4 (d,e). (f) Representative microphotographs showing minor salivary gland sections of a patient with pSS and focus score 4 stained with control isotype antibody. (g) Correlation of IL-36α+ cells with the focus scores. Number of IL-36α-expressing cells was correlated with the ratio between the number of IL-36+ cells and the number of infiltrating mononuclear cells in minor salivary glands of pSS. The r2 (r2 = 0·5460) and P (P = 0·0002) values were determined with Spearman’s correlation coefficient. (h–k) Representative microphotographs showing IL-38 immunostainings in 20 control subjects and 35 pSS patients. (h) In control subjects IL-38 was observed exclusively among ductal epithelial cells. (i–k) In pSS patients a strong expression of IL-38 was observed among acinar epithelial cells and infiltrating mononuclear cells. (l) Representative microphotographs showing minor salivary gland sections of a patient with pSS and focus score 4 stained with control isotype antibody. (m) Quantification of IL-38+ cells in pSS and non-Sjögren’s syndrome patients (nSS). (a–d,f,h–j,l) Original magnification ×250; (e,k) original magnification ×400.
