Figure 2.
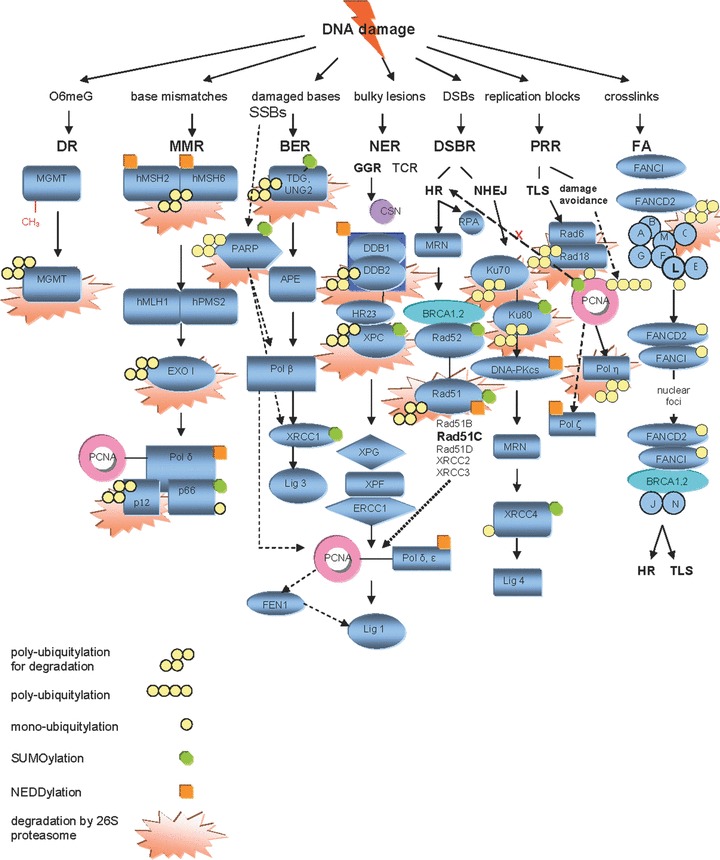
Post-translational modifications of DNA repair by UPS. The regulatory roles of UPS exerted on DNA repair on the post-translational level include (A) signalling for chromatin recruitment (FANCD2-FANCI, XRCC4 mono-ubiquitylation), (B) stabilisation and sustain of activity (XPC, Rad52 SUMOylation), (C) facilitation of DNA unbinding and turnover (TDG, XPC SUMOylation), (D) choice of sub-pathway (PCNA mono-, poly-ubiquitination, SUMOylation) and (E) degradation of DNA repair proteins considered to be proteolytic targets of the proteasome, in a way that both their levels and availability in DNA repair complexes are modified after completion of repair (MGMT, hMutSa complex, hEXO1b, TDG, UNG2, PARP-1, XPC, Rad51, Ku70, Ku80, Rad18, FANCC). There is both proteolytic and non-proteolytic contribution of UPS to this regulation of DNA repair proteins. The first is affected via the attachment of several Ub molecules and subsequent recognition and degradation by the proteasome, while the second is orchestrated through conjugation of the repair protein with a single Ub or Ub-like modifier (mainly SUMO and NEDD8).
