Fig. 3.
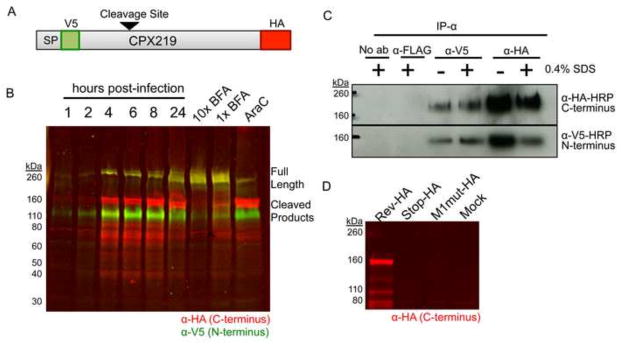
Expression of CPXV219. (A) Diagram of the CPXV219 protein containing a V5 epitope tag immediately after the predicted SP and an HA epitope tag just before the termination codon expressed by CPXV V5-219-HA. The arrow indicates the predicted cleavage site. (B) Western blots. HeLa cells were infected with 3 PFU per cell and whole cell lysates were collected at the indicated hours. In parallel, cells were pretreated and infected with 5 μg/ml (1X) or 50 μg/ml (10X) of BFA or 40 μg/ml AraC for 24 h. The infected cells were lysed with β-mercaptoethanol and SDS and the proteins were resolved by SDS-PAGE. The proteins were transferred to a membrane, probed with antibodies to the V5 (green) and HA (red) epitopes and visualized by infrared fluorescent imaging. Yellow indicates coincidence of V5 and HA antibodies. (C) Association of N- and C-terminal fragments. HeLa cells were infected with 5 PFU per cell of CPXV V5-219-HA for 24 h, harvested in non-denaturing lysis buffer, and incubated with anti-V5 or anti-HA MAb in the presence or absence of 0.4% SDS. Antibody complexes were bound to magnetic protein G Dynabeads and then analyzed by SDS-PAGE and Western blotting. (D) Absence of internal initiation. BS-C-1 cells were infected with 5 PFU per cell of CPXV 219RevHA, CPXV 219Stop-HA and CPXV M1mut-HA. After 24 h, whole cell lysates were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and Western blotting using antibody to the HA epitope tag, and visualized by infrared fluorescence. The positions of marker proteins are shown on the left of each panel.
