Figure 4.
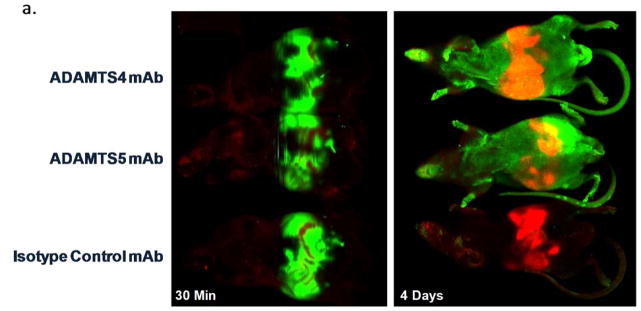
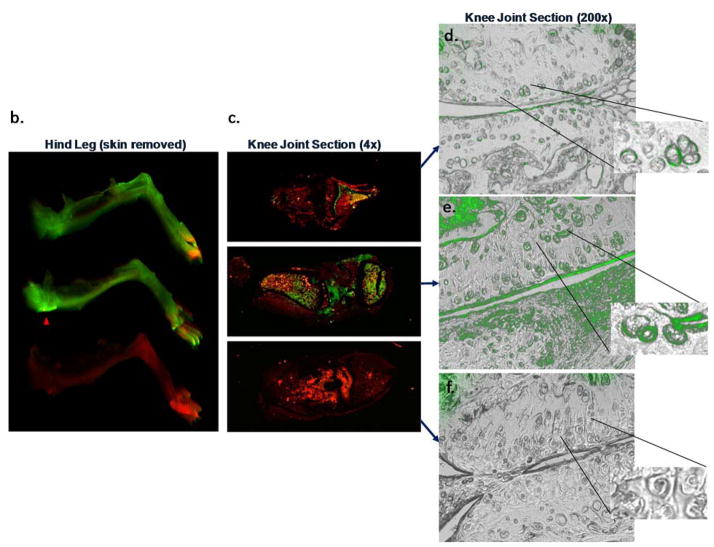
ADAMTS-4 and ADAMTS-5 mAbs engage their targets within the cartilage following systemic administration in a mouse OA model. IR800-labeled ADAMTS-4 (7E8.1E3), ADAMTS-5 (7B4.1E11) or Isotype control mAbs were administered ([16mg/kg] IP) to mice (n=1/group) six weeks after surgical destabilization of the medial meniscus and periodically imaged to monitor systemic biodistribution and tissue penetration. Within 30 minutes of dosing a strong IR800 signal (green) can be observed in the abdomen of all animals (a, left) indicative of accurate administration. The red abdominal signal is related to the inherent infrared signature of the animal diet traversing the digestive system. Systemic IR800 signal is observed in mice receiving ADAMTS-4 or ADAMTS-5 mAb (and to a much lesser extent the isotype control treated animal) 4 days following administration (a, right) when the animals were sacrificed to assess tissue distribution. The right hind leg of each animal is shown (b) with skin removed showing a strong signal intensity in the joint region of the ADAMTS-5 mAb treated mouse (red arrowhead) compared to the other treatments. Similar qualitative differences between treatment groups can be observed in low (c; 4X magnification) and high power (d–f; 200X magnification) images of the knee joint, as well as evidence for cartilage penetration and deposition in the cartilage for the ADAMTS-4 and ADAMTS-5 mAbs in the superficial cartilage zone and pericellular region of the articular chondrocytes (d–e, inset). Merged microscopic bright-field/IR800 images are shown. In the ADAMTS-5 mAb panel (e) staining in the meniscus can be observed (bottom half of image). No signal was observed following administration of a labeled isotype control mAb (f) or following administration of a non-reactive dye control, which was undetectable within 24 hours after dosing (not shown).