Figure 2.
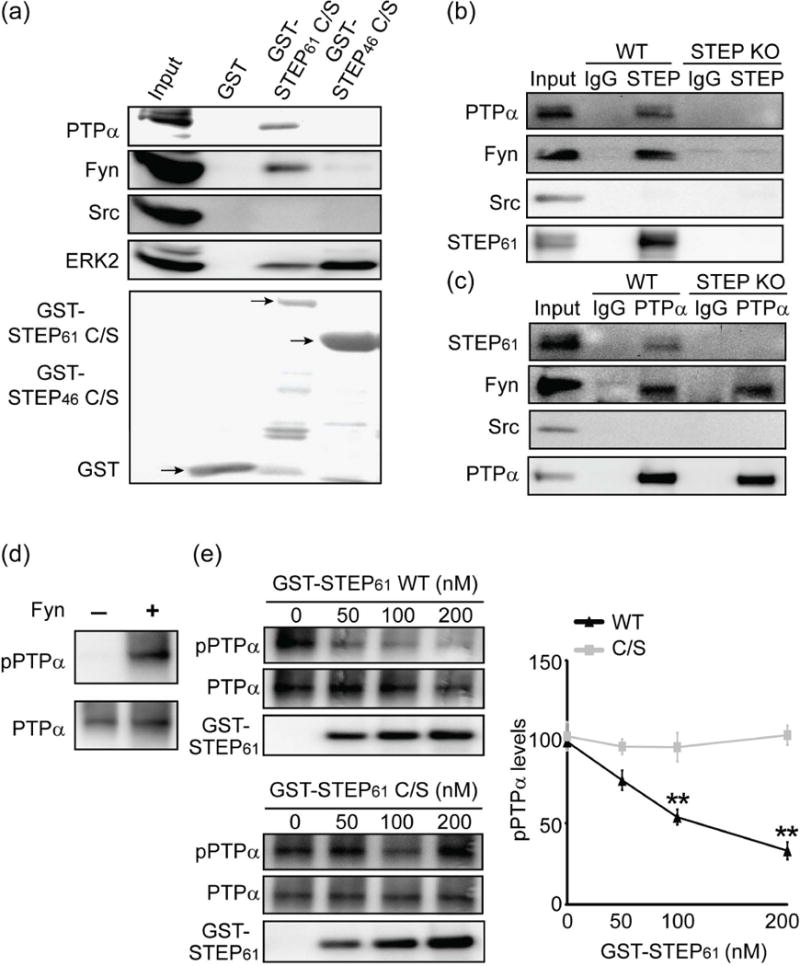
STEP61 binds to and dephosphorylates PTPα at Tyr789. (a) The substrate-trapping (C472S) mutants STEP61 C/S and STEP46 C/S or GST tag alone were adsorbed to glutathione sepharose beads and incubated with mouse striatal homogenates. Bound proteins were visualized with specific antibodies as indicated in the figure. (b, c) STEP61 is associated with PTPα in mouse striatum. WT or STEP KO mouse striatal lysates (300 μg) were incubated with mouse IgG and anti-STEP (23E5) mouse monoclonal antibody (b) or goat IgG and anti-PTPα goat polyclonal antibody (c) overnight at 4 °C. Co-immunoprecipitation of STEP interacting proteins (b) or PTPα interacting proteins (c) was probed with antibodies indicated in the figure. Thirty μg of WT striatal lysates were used as input. Representative blots were shown from three independent experiments (n = 3). (d) Recombinant PTPα was phosphorylated by Fyn in vitro. (e) STEP61 dephosphorylates PTPα at Tyr789. In vitro phosphorylated recombinant PTPα was incubated with active STEP61 (WT) or inactive STEP61 (C/S). The residual phosphorylation of PTPα at Y789 was assessed using a phospho-specific antibody. Data were expressed as mean ± SEM (WT versus C/S at the same dose: **p < 0.01, one-way ANOVA with post hoc Tukey’s test; n = 4).
