Figure 3.
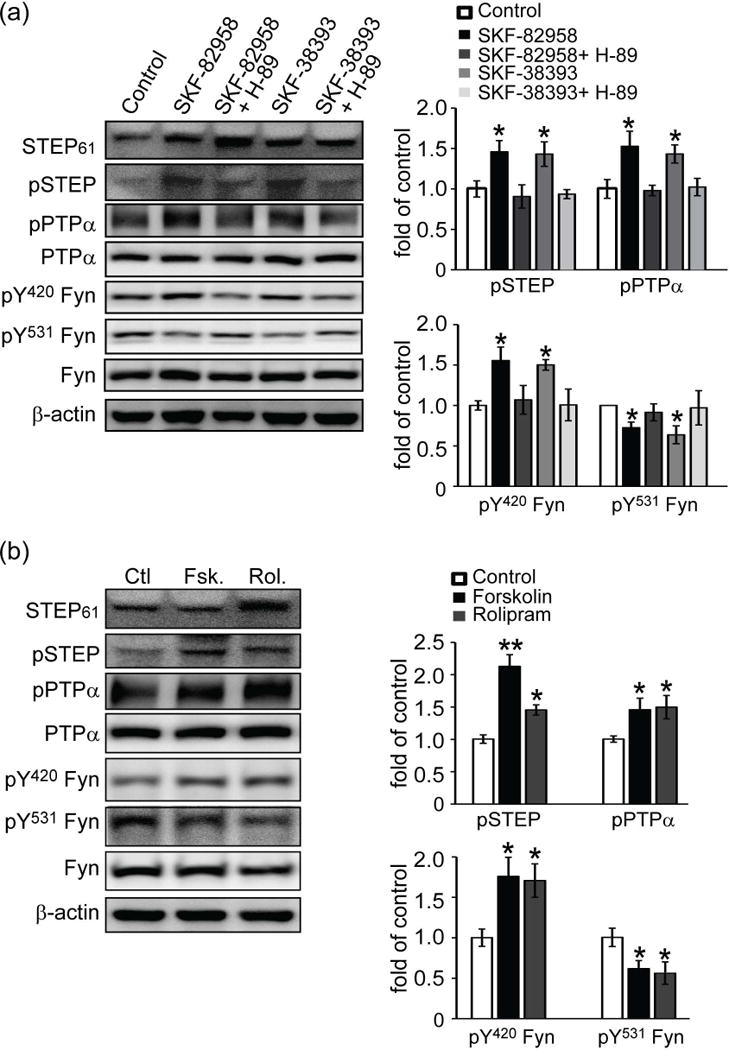
Inactivation of STEP61 results in increased phosphorylation of PTPα. (a) D1 dopamine receptor activation leads to PKA-mediated phosphorylation and inactivation of STEP61. Corticostriatal neurons were treated with SKF-82958 (10 μM) or SKF-38393 (10 μM) for 30 min. Some cultures were preincubated with H-89 (10 μM) for 30 min, followed by D1R agonists stimulations. (b) Inhibition of STEP61 leads to increased phosphorylation of PTPα. Neurons were treated with forskolin (Fsk, 100 μM, 10 min) and rolipram (Rol, 1 μM, 30 min) prior to western blotting. Phospho-protein and total protein levels were assayed with phospho-specific and pan-antibodies as indicated. Phospho-proteins were normalized to total protein levels and then to β-actin as a loading control. All data were compared to controls and expressed as mean ± SEM and statistical significance was determined with one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s test (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01; n = 4).
