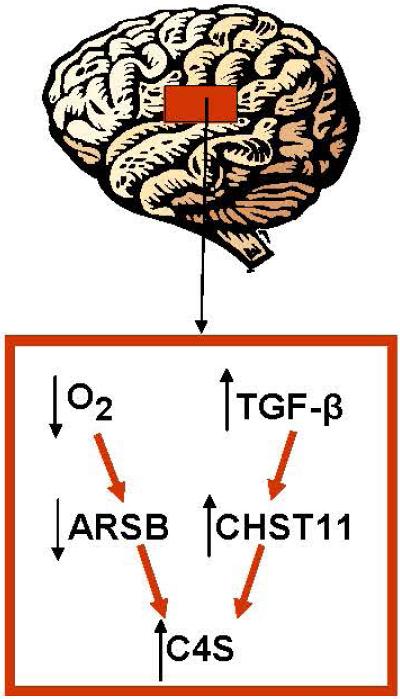
Fig. 8. Schematic showing two pathways by which chondroitin 4-sulfate increases post-TBI.
C4S increases due to reduced degradation and increased synthesis. Reduced degradation is attributable to hypoxia-induced decline in ARSB activation following injury, with disruption of normal tissue oxygenation and structure, leading to accumulation of more highly sulfated C4S. C4S also accumulates due to increased synthesis from TGF-β1-induced increase in CHST11 expression with increased sulfotransferase activity.