Fig. 2. The deletion of COQ9 in a yeast coq5-5 point mutant leads to the accumulation of 3-hexaprenyl-4-aminophenol (4-AP) and the disappearance of demethyl-demethoxy-Q6 (DDMQ6), but imino-demethyl-demethoxy-Q6 (IDDMQ6) is still present.
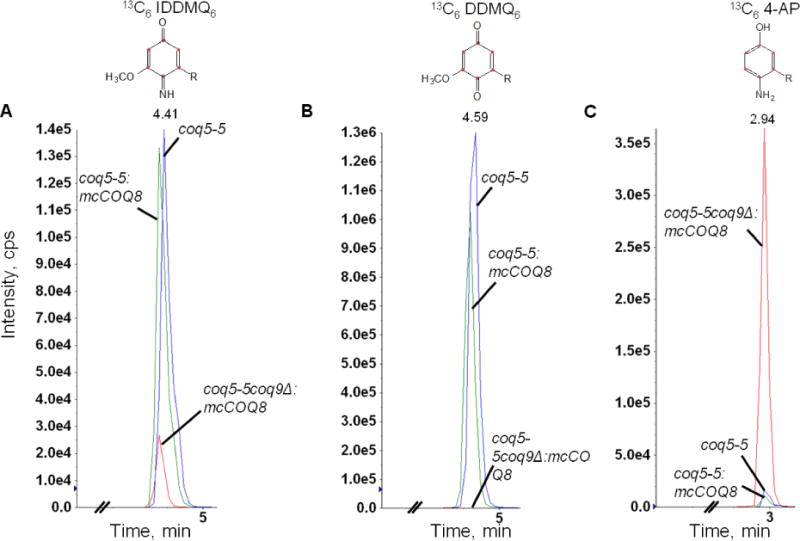
Yeast coq5-5 point mutants with COQ8 over-expressed (coq5-5:mcCOQ8), without COQ8 over-expressed (coq5-5), or with the COQ9 gene deleted and COQ8 over-expressed (coq5-5 coq9Δ:mcCOQ8), were cultured in SD complete or SD−Ura with 50 μg/ml 13C6-pABA and 2 μl ethanol/ml medium at 0.5 A600nm/ml and collected after 6 hours. Q4 (145.4 pmol) was added prior to extraction to serve as an internal standard. Lipid extracts prepared from the cell pellets were analyzed by RP-HPLC-MS/MS. Multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) detected precursor-to-product ion transitions 552.4/158.0 (13C6 –IDDMQ6), 553.4/159.0 (13C6-DDMQ6), and 524.4/128.0 (13C6-4-AP). Just the oxidized forms of IDDMQ6 and DDMQ6 were detected, while only the reduced form of 4-AP was present. 13C6-DDMQ6 accumulates in the coq5-5 and coq5-5:mcCOQ8 yeast mutants (B), and 13C6-IDDMQ6 is readily detected (A). 13C6-IDDMQ6 and 13C6-4-AP accumulate in coq5-5 coq9Δ:mcCOQ8 (A and C), but 13C6-DDMQ6 is not detected (B). In all panels, the blue traces designate the Q-intermediate signals in coq5-5 and green traces designate the Q-intermediate signals in coq5-5:mcCOQ8, and the red traces indicate the Q-intermediate signals in coq5-5 coq9Δ:mcCOQ8.
