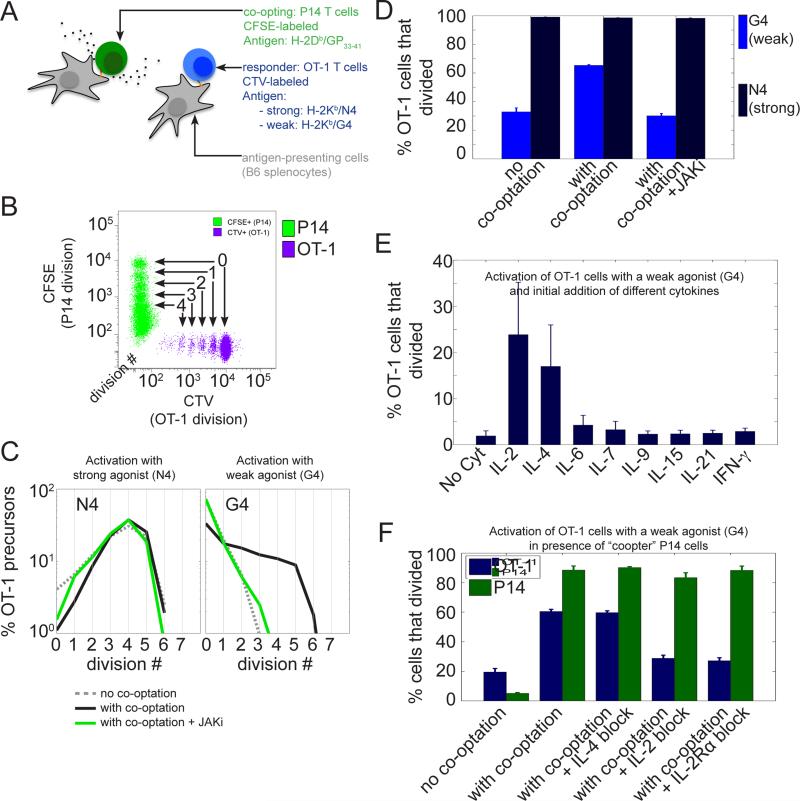
Fig.1. The inter-clonal co-optation of weakly activated CD8+ T cells is dependent on IL-2.
(A) Two different TCR transgenic CD8+ T cell populations (P14 and OT-1) were labeled with different amine reactive dyes (CFSE and CTV respectively) and stimulated in vitro with specific antigens presented by distinct APCs.
(B) Tracking of the proliferation of the two different T cell populations by flow cytometry using the dilution of a fluorescent amine reactive dye (CFSE for P14 cells and CTV for OT-1 cells). Representative dot plot of CFSE and CTV MFI for live CD8+ cells after 3 days of co-culture. At each cell division, the amount of the amine reactive dye per cell is divided uniformly by a factor 2 amongst daughter cells, which allows one to track the number of divisions experienced by a given cell until the time of observation and to estimate the number of divisions performed by precursor cell.
(C and D) Activated P14 cells co-opt only weakly stimulated OT-1 cells and this is conditioned upon JAK signaling. (C) Distributions of the number of cell divisions per OT-1 precursor cells after 3 days in the in vitro co-culture system presented in (A) and (B). OT-1 cells were stimulated with Kb MHC loaded with either a strong (N4, peptide sequence : SIINFEKL) or a weak agonist (G4, peptide sequence : SIIGFEKL). For each condition of stimulation for the OT-1 cells, the co-cultured P14 cells were either not stimulated (‘no co-optation’ condition), or stimulated with their cognate antigen GP33-41 (‘with co-optation‘ condition) in the presence or absence of a JAK inhibitor (AZD1480, 1uM). (D) Representation of the percentage of OT-1 precursor cells that divided for the experiment shown in (C). Error bars represent mean +/− SD for three replicates; the results are representative of n≥3 independent experiments.
(E) Effect of the addition of different cytokines on the proliferation of OT-1 cells stimulated with the weak agonist Kb/G4 in the absence of ‘co-opting’ P14 cells. A given dose of cytokine (1nM) was added at time t=0 and the number of OT-1 precursors that divided was estimated after 3 days. Error bars represent mean +/− SD for three replicates; the results are representative of n≥3 independent experiments. Amongst the cytokines tested, IL-2 and IL-4 were found to be the only ones to allow a significant fraction of weakly stimulated OT-1 cells to proliferate.
(F) IL-2 and not IL-4 is responsible for the co-optation of OT-1 cells by P14 cells. OT-1 cells were stimulated with a weak agonist (Kb/G4) in the presence of P14 cells left either unstimulated (‘no co-optation‘) or stimulated by their cognate antigen Db/GP33-41 (‘with co-optation‘). Blocking antibodies against Mouse IL-2 (clone JES6-1A12) and IL-4 (clone 11B11) were added at time t=0 to identify the cytokines mediating the co-optation of OT-1 cells. The effect of IL-2 blockade was confirmed using a blocking antibody against the alpha subunit of the IL-2 receptors (CD25, clone PC61.5). Error bars represent mean +/− SD for three replicates; the results are representative of n≥3 independent experiments.