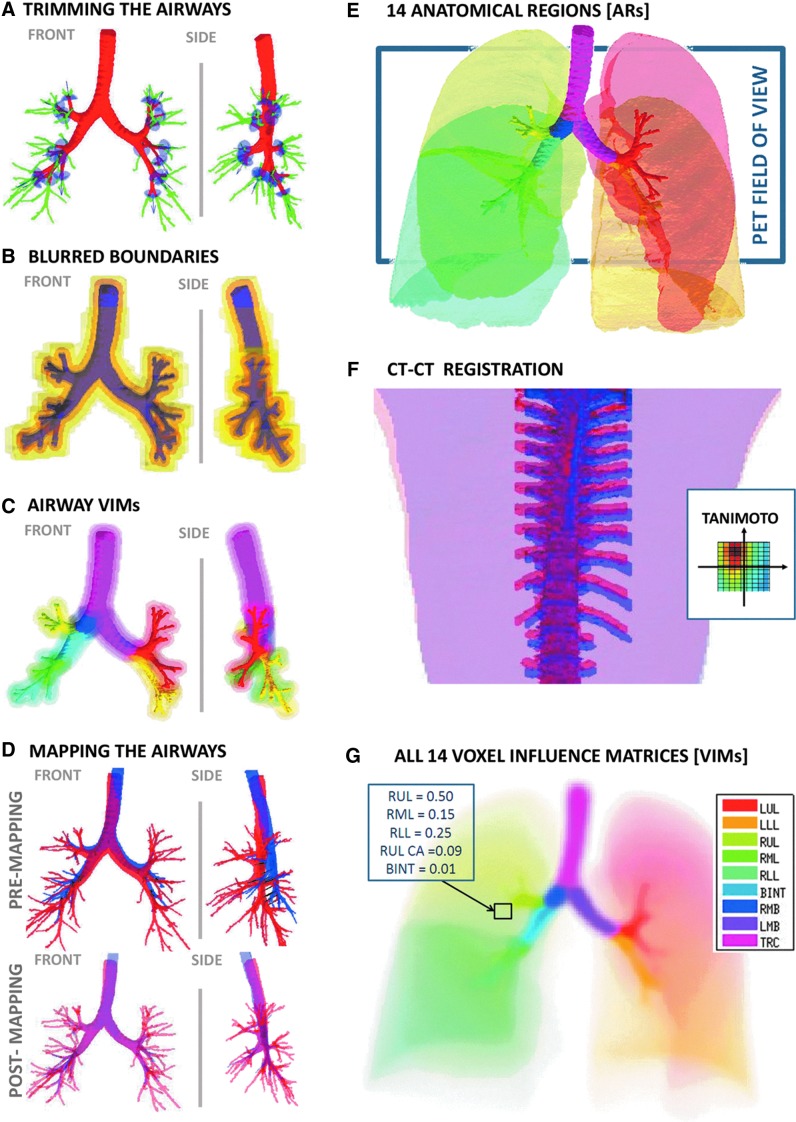
FIG. 1.
Panels illustrate the methods. (A) The TLC airway tree is trimmed to the sub-segmental generation to obtain a central airway tree ROI that is consistent across subjects. In light blue are umbrella-shaped cutting elements oriented with the segmental airways. In green are the trimmed portions of the tree. (B) The boundaries of the airways before and after the addition of sequential sources of blurring; the trimmed TLC @ MLV airway tree (purple), motion blur (light purple), PET blur (orange), including transformation and registration error (darker yellow), and the final PET mask discretized to the PET deposition image (light yellow). The boundaries represent the point where the voxel VI >0.1%. (C) The nine airway tree ARs (shown in saturated colors), and iso-contours of their corresponding VIMs in matching colors representing 10%, 1%, and 0.1% VI are drawn for each AR (the color legend is shown in panel G). (D) Effect of mapping airway tree from TLC to MLV: Front and lateral projections of the airway tree (Top) rendered from a CT acquired at TLC (red) and one at MLV (blue); (Bottom) the same as above, but with the TLC tree mapped to the MLV. (E) A Rendering of the 14 Anatomical Regions (ARs). The color legend is shown in panel G. The lobar central airways are color matched to the lobes that they feed. The 16 cm PET field of view and the typical placement of the PET image are shown with the rectangle. The lung volume for this subject was 4.7 L at MLV (average volume at MLV was 3.2 L). (F) The co-registration of the TLC (red) and MLV (blue) spines. The inset shows the variability in the Tanimoto Similarity Coefficient of the upper spines as the images are shifted relative to each other. The dark spot shows that the HRCT images are best co-registered when the blue spine is shifted up and to the left. (G) A visualization of the VIMs. Each color indicates the VIM of a single AR. VIMs estimate of how homogenous activity within an AR appears in the radionuclear image. Where in a conventional black or while ROI each voxel is assigned to a specific AR, the rectangle shows how the voxel is influences by many ARs.