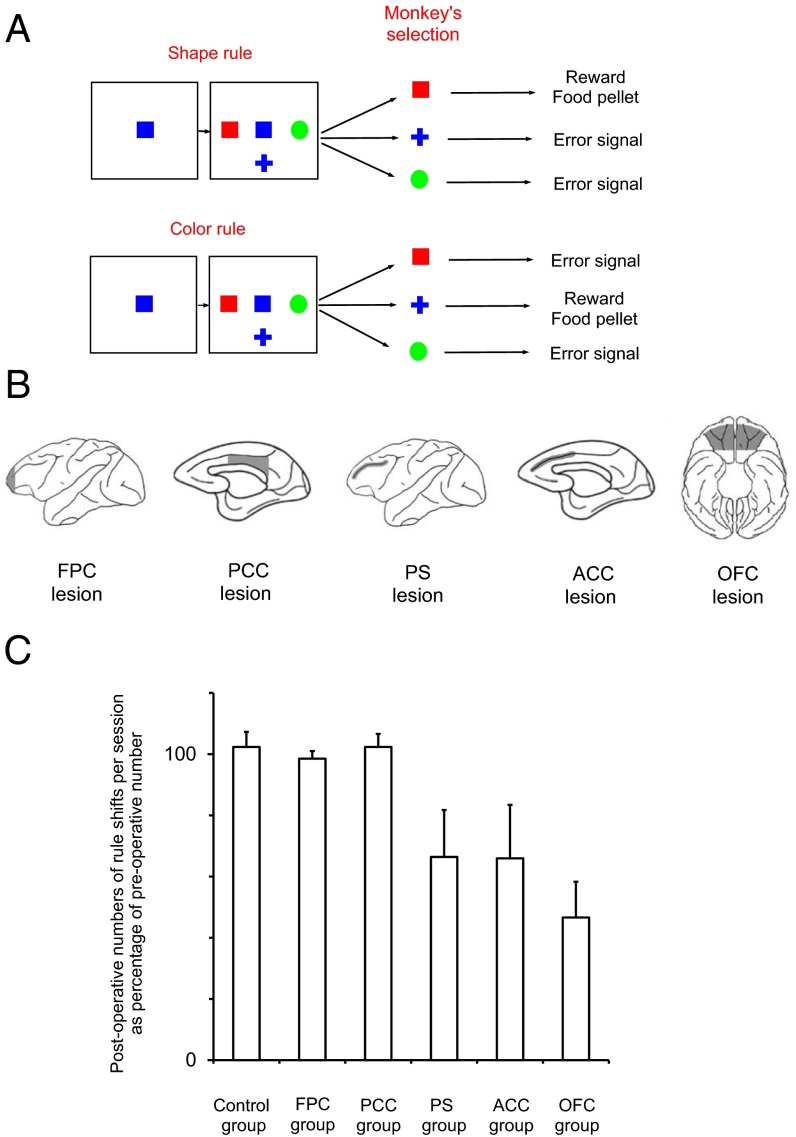
Fig. 1.
Intended lesion extend, task procedures, and overall performance in the standard WCST analog. (A) In each trial, a sample was presented, and when the monkey touched the sample, three test items appeared surrounding the sample. One test item matched the sample in color but not in shape, a second matched in shape but not in color, and the remaining one did not match in either color or shape. Sample and test items were randomly selected from a set of 36 stimuli made by combining six colors and six shapes. The monkeys had to touch the test item that matched the sample either in color or shape, depending on the currently relevant rule, within 3,000 ms to receive a food reward. If the monkey made an incorrect choice, a white circle appeared for 1,000 ms as an error signal, and no reward was provided. The intertrial interval was 6 s after correct responses and 12 s after erroneous responses. The matching rule changed every time that the animal attained 17 corrects in 20 consecutive trials (shift criterion). (B) The extents of cortical lesions indicated by the shaded areas in the brain diagrams. (C) The mean number of postoperative rule shifts achieved per daily session is expressed as a percentage of the mean number of preoperative rule shifts in each monkey for the control group (n = 3) and monkeys with lesions within the FPC (n = 4), PCC (n = 3), PS cortex (n = 4), ACC (n = 4), or OFC (n = 3). The data of PS, ACC, and OFC groups were obtained from our previous study with the same task (42). Error bars indicate the SEM across monkeys in each group.