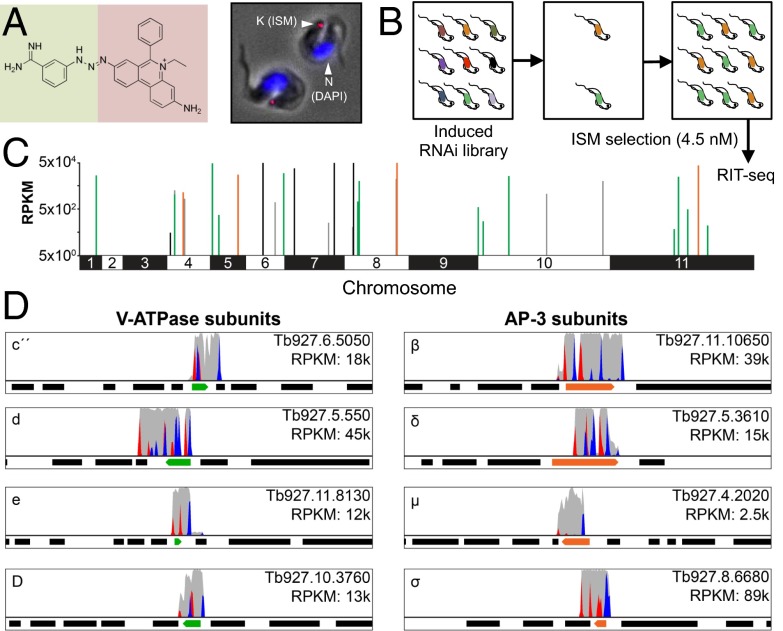
Fig. 1.
An RNAi screen implicates acidic compartment defects in isometamidium resistance. (A) The ISM structure is shown on the left, indicating the coupling of homidium (ethidium, pink background) with the p-aminophenyl-diazonium portion of diminazine (berenil, green background). T. brucei stained with ISM (red) and DAPI (blue) are shown on the right. K, kinetoplast; N, nucleus. ISM quenches the DAPI signal that would otherwise also stain the kinetoplast. (B) The schematic illustrates the genome-scale RNAi-library screen. RNAi was induced with tetracycline. RIT-seq, RNA-interference target sequencing. (C) The genome-wide RIT-seq map indicates hits from the RNAi screen; loci identified by >100 sequence reads that contain the RNAi vector barcode. V-ATPase, AP-3, and EMC subunits are indicated in green, orange, and black, respectively. See Table S1 for the full list. RPKM, reads per kilobase per million reads mapped. (D) The Artemis screen-shots show example hits in green and orange; flanking protein coding sequences are indicated as black bars. Red peaks, forward reads with RNAi-construct barcodes; blue peaks, reverse reads with RNAi-construct barcodes; gray peaks, all other reads.