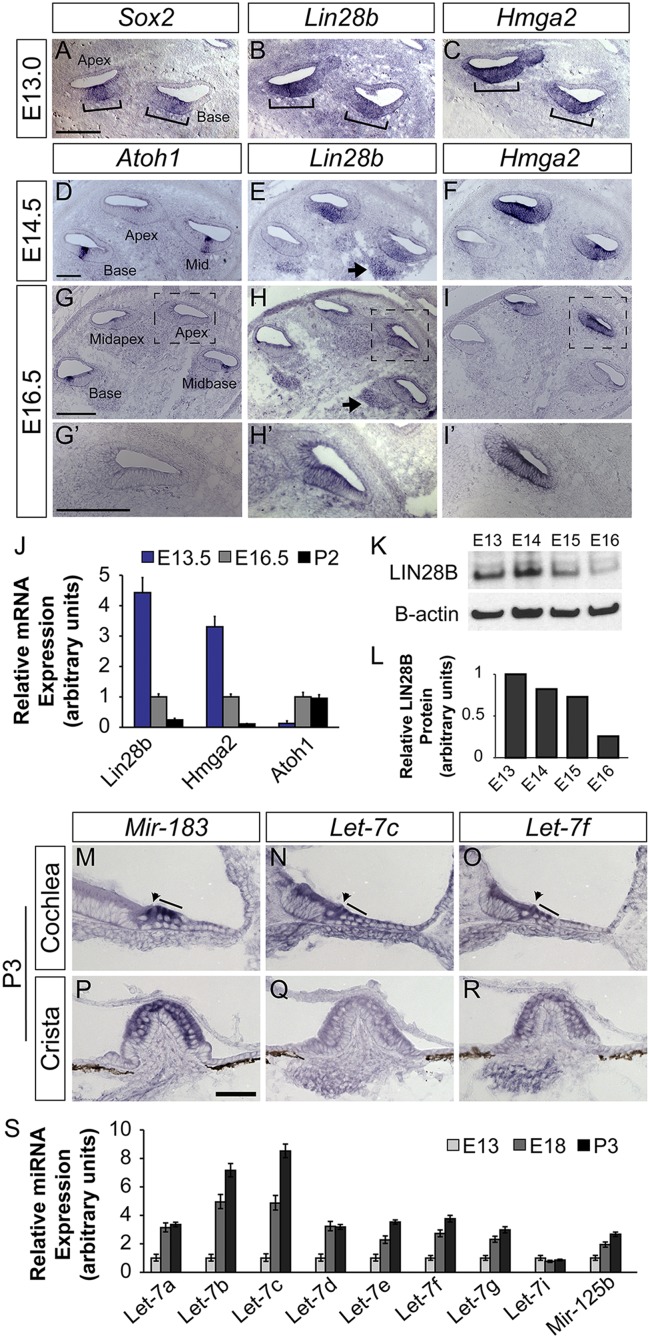
Fig. 1.
Members of the Lin28b/let-7 axis are differentially expressed in the developing cochlea. (A–I′) ISH-based analysis of Lin28b and Hmga2 expression before (A–C) and during cochlear differentiation (D–I′). Sox2 (A) marks prosensory cells, and Atoh1 (D, G, and G′) marks HCs. Brackets (A–C) indicate the prosensory domain. Arrows (E and H) indicate Lin28b expression within the developing spiral ganglion. High power images of the apical turn of G–I are shown in G′–I′. (J) RT-qPCR analysis of relative Lin28b, Hmga2, and Atoh1 mRNA expression within the cochlear epithelium before (E13.5), during (E16.5), and following (P2) differentiation. Rpl19 was used as an endogenous reference gene. Data are mean ± SEM. (K and L) LIN28B protein quantification within the cochlea epithelium at stages acutely surrounding the onset of HC differentiation. (M–R) ISH-based analysis of let-7c and let-7f expression within the early postnatal (P3) cochlea (M–O) and vestibular crista (P–R). Mir-183 (M and P) marks cochlear and vestibular HCs. Arrowheads and lines (M–O) indicate cochlear IHCs and OHCs. (Scale bars: A–I′, 100 μm; M–R, 50 μm.) (S) RT-qPCR analysis of mature let-7 miRNA expression within the cochlear epithelium before (E13), during (E18), and following (P2) differentiation. The snoRNA U6 was used as an endogenous control. Data are mean ± SEM.