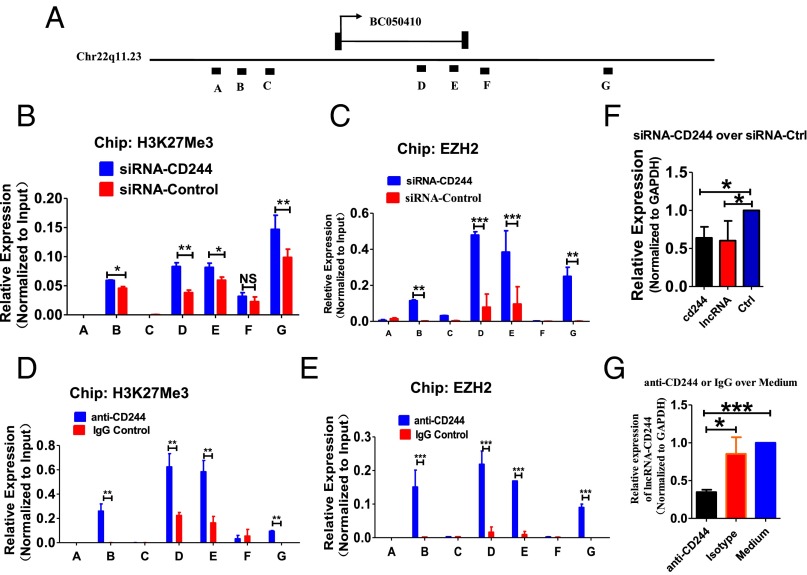
Fig. 4.
Knock down of CD244 or blockade of CD244 signaling induces a more repressive chromatin state in lncRNA-CD244 locus and inhibits expression of lncRNA-CD244. Seven regions (capital letters A to G) across lncRNA-CD244 locus, as shown in A, were analyzed in ChIP-qPCR analyses for H3K27Me3 (B and D) histone modification and EZH2 (C and E) in PBMCs from patients with active TB. PBMCs were transfected with siRNA-CD244 or siRNA-Ctrl or treated with anti-CD244 mAb or IgG control as indicated in each of subfigure. Values derived from three independent experiments were normalized by background signals and input chromatin. (F and G) qPCR analysis of lncRNA-CD244 and/or the cd244 gene in PBMCs from patients with active TB transfected (or treated) with indicated siRNAs (F) or antibodies (G). Data are presented as relative expression levels of lncRNA-CD244 (or cd244) (normalized to GAPDH) in siRNA-CD244–transfected (or anti-CD244–treated) PBMCs over expression levels of lncRNA-CD244 (or cd244) in siRNA-Ctrl–transfected (or IgG-treated) PBMCs (n = 7). *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; NS, no statistical significance. Error bars represent SEM from three independent experiments.