Fig. S9.
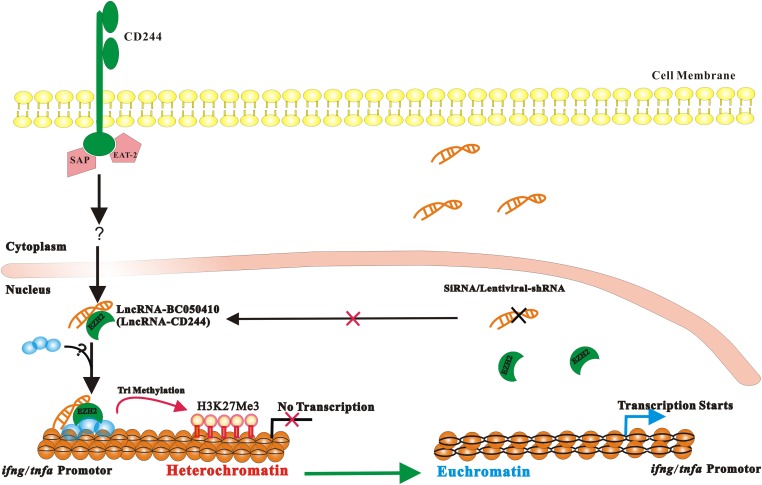
A proposed model of ifng and tnfa expression regulated by lncRNA-CD244 in CD8+ T cells during active TB infection. TB infection induces up-regulation of CD244 on CD8+ T cells, which drives expression of lncRNA-CD244. lncRNA-CD244 that localizes in the nucleus mediates recruitment of polycomb protein EZH2 to trimethylate H3K27 at promoter of IFN-γ and TNF-α, which therefore induces a repressive chromatin (heterochromatin) in ifng and tnfa locus, and therefore transcription of ifng and tnfa is inhibited. Knock down of lncRNA-CD244 using siRNA or LV vector encoding shRNA targeting lncRNA-CD244 results in failure of recruitment of EZH2 to promoter of IFN-γ and TNF-α, and therefore heterochromatin is changed to euchromatin and transcription of ifng and tnfa starts. It remains unclear whether lncRNA-CD244 mediates recruitment of EZH2 alone or with other histone modification enzymes. SAP and EAT-2 are associated with CD244 signaling in active TB, but it remains unknown which molecules are downstream of CD244-SAP/EAT-2 signaling cascades.