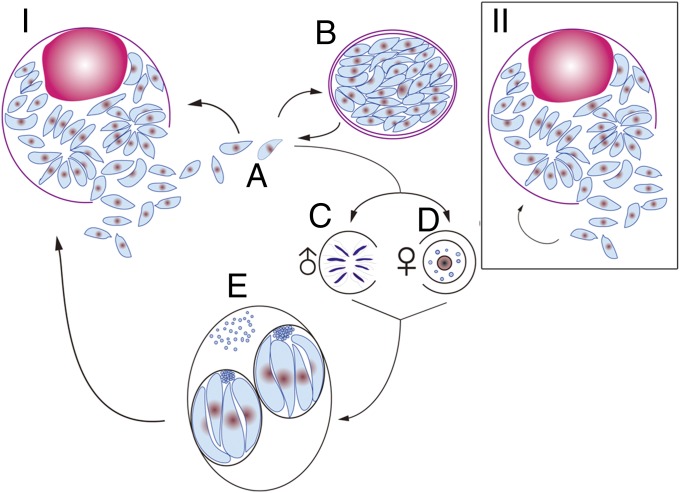
Fig. 3.
(I) Life cycle of WT T. gondii. Tachyzoites (stage A) can differentiate into bradyzoites (stage B) in definitive or intermediate hosts and can differentiate into oocysts (stage E) in the definitive host (feline animals, cats) after sexual reproduction (stages C and D). Both parasite and host can survive in most cases depending on the life span of the host. (II) RH strain, a mutant strain of WT T. gondii. The tachyzoite (stage A) cannot differentiate into the bradyzoite in either the intermediate or the definitive host and cannot differentiate into oocysts in the definitive host. It reproduces by reinfection of host cells (stage B). The hosts will normally be killed by the parasites or vice versa.