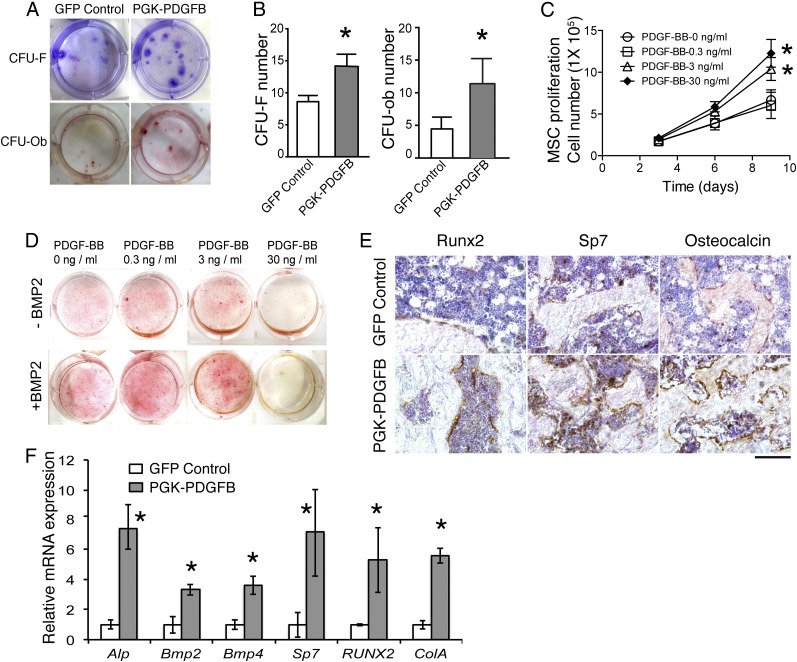
Fig. 4.
The PDGF-BB therapy promotes bone formation by increasing numbers of MSC, preosteoblasts and osteoblasts, as well as enhancing osteogenesis-related gene expression. (A) Representative images of CFU-F colonies stained with Crystal violet (Upper) and CFU-Ob colonies stained with Alizarin red (Lower). CFU-F and CFU-Ob assays were conducted with bone marrow cells harvested from GFP control or PGK-PDGFB–treated mice. (B) Quantification of the CFU-F and CFU-Ob numbers. GFP control vs. PGK-PDGFB, *P < 0.05. (C) MSC proliferation curve. GFP control vs. PDGF-BB (3 or 30 ng/mL), *P < 0.05. (D) Alizarin red staining for osteoblastic differentiation of MSCs. Bone nodule formation was enhanced by PDGF-BB protein at 0.3 ng/mL and 3 ng/mL when BMP2 was added, but reduced by PDGF-BB at 30 ng/mL. Red stained are bone nodules after 3 wk of culture in osteogenic medium. (E) Immunohistochemical staining for Runx2, Sp7, and osteocalcin on thin sections of mouse femurs. (Scale bar, 100 μm.) (F) Real-time qPCR analysis of osteogenesis-related genes in the tibias. GFP control vs. PGK-PDGFB, *P < 0.05.