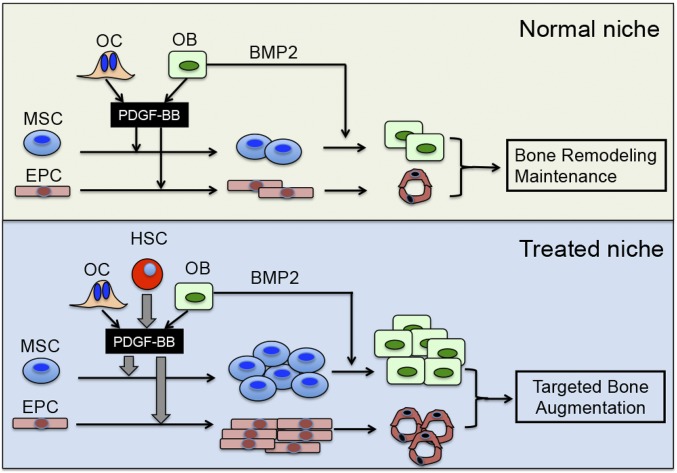
Fig. 6.
Schematic diagram of PDGFB-Sca1+ cells induced bone formation at the endosteal niche. (Upper) Normal niche: Under normal conditions, PDGF-BB produced by osteoblasts and osteoclasts/preosteoclasts (and perhaps other local cells) promotes the proliferation of MSCs and endothelial progenitor cells. (Lower) Treated niche: The intravenously injected PDGFB–Sca1+ cells homed to the HSC niche at the endosteum following preconditioning. After engraftment in the niche, the HSCs constitutively produce large amounts of PDGF-BB (large gray arrow), which acts as potent mitogen for nearby MSCs and endothelial progenitor cells. The local production of the Bmps is sufficient to promote the differentiation of MSCs ultimately to osteoblasts. PDGF-BB may also activate Bmp signaling in osteoblasts. As a result, there is a robust increase in endosteal bone formation (Lower, treated niche). We propose the same sequence of events for the perivascular niches, which leads to increased trabecular bone formation.