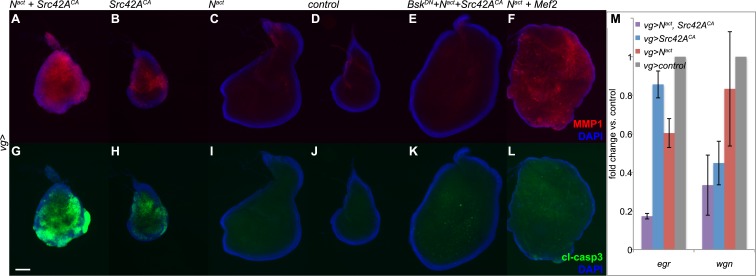
Figure 3. N/Src synergy induces both MMP1 and apoptosis.
(A–L) Immunofluorescence for MMP1 (A–F) and cleaved caspase 3 (cl-casp3, G–L) in wing discs expressing UAS constructs under vgGal4. Together, Nact and Src42ACA cause robust activation of both MMP1 (A) and cl-casp3 (G), which is strongly reduced by BskDN (E, K). The combination of Nact and Mef2 results in an increase in MMP1 (F) but little effect on cc3 (L). (M) qPCR for egr and wgn in wing discs overexpressing genes as indicated under the vgGal4 driver reveals that both transcripts are strongly downregulated when Nact and Src42ACA are coexpressed. Scale bar: 100 μm.