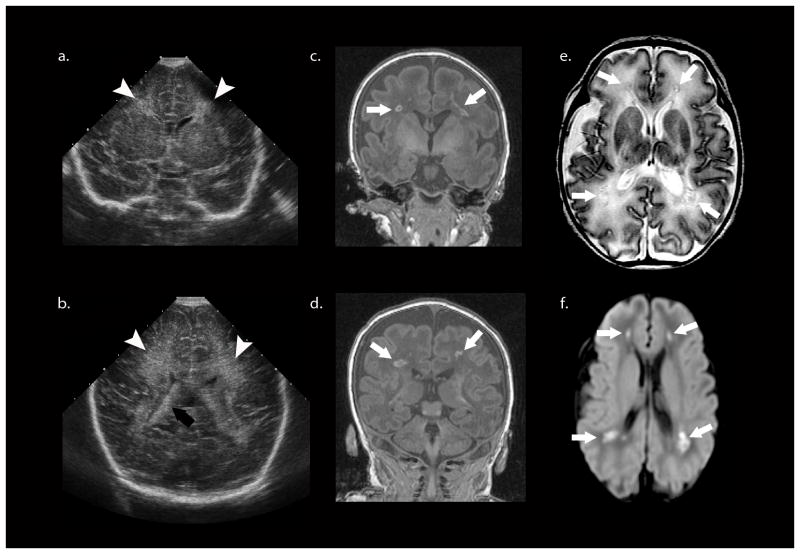
Fig. 3.
More recent case of periventricular leukomalacia. a, b Cranial US shows slightly increased diffuse periventricular echogenicity (white arrowheads) relative to the choroid plexus (black arrow) and no other abnormality. c, d Coronal SPGR MR (in plane resolution 0.625 mm × 0.625 mm with slice thickness of 1.5 mm) performed the same day as cranial US with a neonatal head coil shows multiple foci of high T1 signal (white arrows) in the deep/periventricular white matter that likely represent focal white matter necrosis or non-cystic PVL. e These lesions (white arrows) demonstrate low T2 signal intensity surrounded by T2 hyperintensity, which could represent diffuse injury or unmyelinated white matter. f The trace image from the diffusion weighted MRI scan shows that the focal lesions (white arrow) are diffusion restricting. The mean diffusivity and fractional anisotropy maps are not shown.