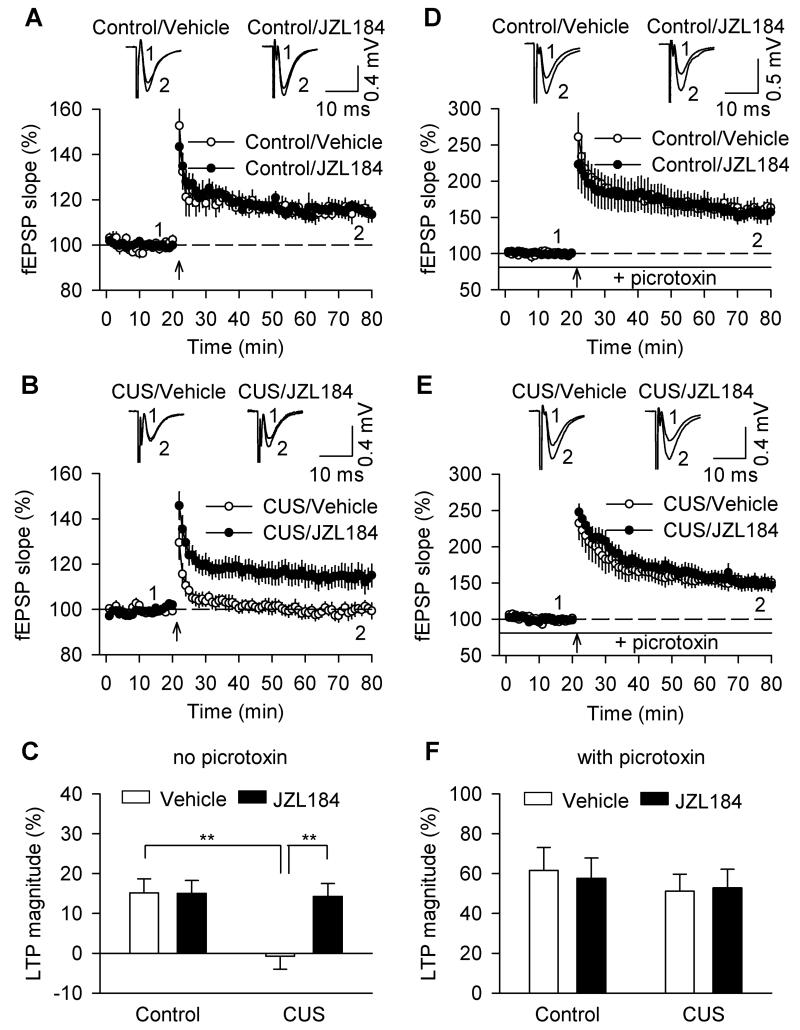
Figure 4.
Effects of CUS and chronic JZL184 treatments on LTP in the DG. (A) In hippocampal slices from control mice, chronic JZL184 treatments did not significantly alter LTP compared with vehicle treatment (n = 7-8 slices/N = 4-5 mice). Sample fEPSPs are shown on the top. (B) In slices from CUS-exposed mice, chronic JZL184 treatments prevented CUS-induced impairment of LTP (n = 8-8 slices/N = 5-6 mice). (C) ANOVA performed on the last 10 min of LTP recording showed that CUS impaired LTP induction, and this effect was prevented by chronic JZL184 treatments (n = 7-8 slices/N = 4-5 mice; **p < 0.01). (D,E) In the presence of picrotoxin (50 μM), robust LTP was induced in slices from vehicle and JZL184-treated control (D) and CUS mice (E). (F) Summarized results showed that neither CUS nor JZL184 had significant effect on LTP induction (n = 7-8 slices/N = 4-5 mice; p > 0.05).