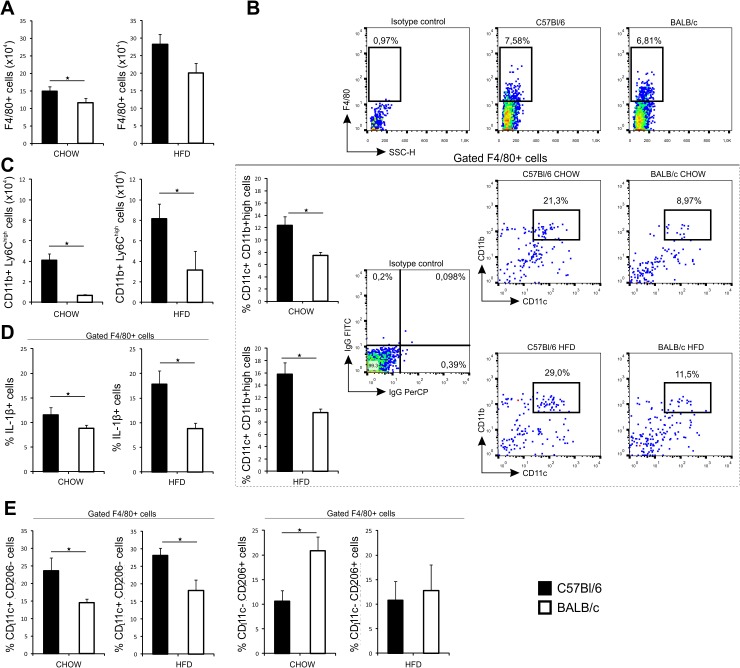
Fig 5. Phenotypic analysis of macrophages in liver in chow and HFD-fed C57Bl/6 and BALB/c mice.
(A) Number of F4/80+ macrophages was significantly higher in chow-fed C57Bl/6 mice compared to chow-fed BALB/c mice at 32 weeks of age. (B) Percentage of triple positive F4/80+ CD11bhigh CD11c+ macrophages was significantly higher in liver of chow- and HFD-fed C57Bl/6 mice compared with diet-matched BALB/c mice at 32 weeks of age. Gating strategy, isotype controls and representative FACS plots of triple positive F4/80+ CD11bhigh CD11c+ cells in liver of C57Bl/6 and BALB/c mice on both diets. (C) Number of CD11b+Ly6Chigh cells was significantly higher in liver of chow- and HFD-fed C57Bl/6 mice compared with diet-matched BALB/c mice at 32 weeks of age. (D) Percentage of IL-1β expressing F4/80+ macrophages was significantly higher in liver in chow- and HFD-fed C57Bl/6 mice compared with diet-matched BALB/c mice at 32 weeks of age. (E) Percentage of CD11c+CD206- cells among gated F4/80+ cells was significantly higher in liver in chow- and HFD-fed C57Bl/6 mice compared with diet-matched BALB/c mice at 32 weeks of age. Percentage of CD11c-CD206+ cells among gated F4/80+ cells was significantly lower in liver of chow-fed C57Bl/6 mice. The results are shown as the means ± SEM of 9–10 animals per group. *p<0.05. The results are representative of two experiments.