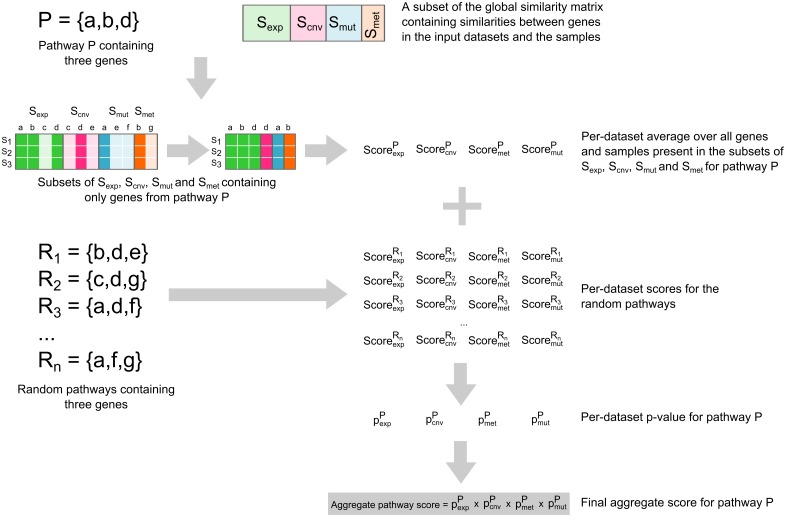
Fig 2. Pathway relevance scoring.
Given a subset of the global similarity matrix (Sexp Scnv, Smut, Smet, see Fig 1) and a set of genes (a,b,d) constituting a pathway P, a score for each input dataset is calculated by first removing genes from Sexp Scnv, Smut, Smet that do not belong to the pathway and then taking the average of all remaining values in Sexp Scnv, Smut, Smet. This process is repeated for n randomly generated gene sets (with the same number of genes as the pathway P) yielding n scores for each input dataset. The random pathway scores are used to calculate a p-value for obtaining the pathway scores purely by chance. The resulting p-values are multiplied, resulting in a single aggregated pathway score.