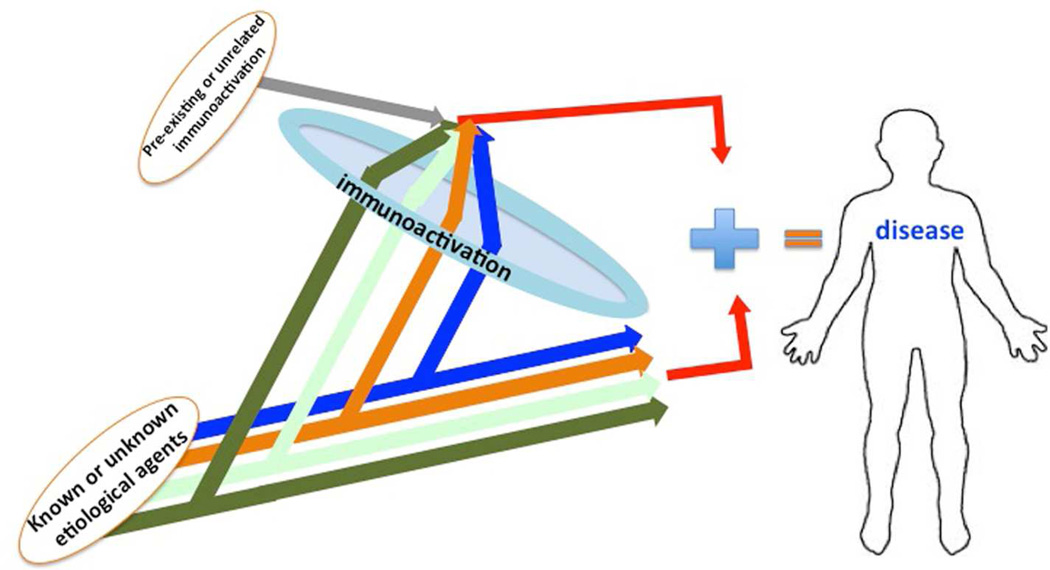
Figure 1. Immunoactivation hypothesis.
Human diseases are triggered by various etiological agents: viruses, bacteria, parasites, or unknown factors causing specific pathologies in the human organism. However, disease progression also requires immunoactivation, which is largely similar for all of them. This immunoactivation can be caused by the same agents or may have been developed prior to and independently of the etiological agent.