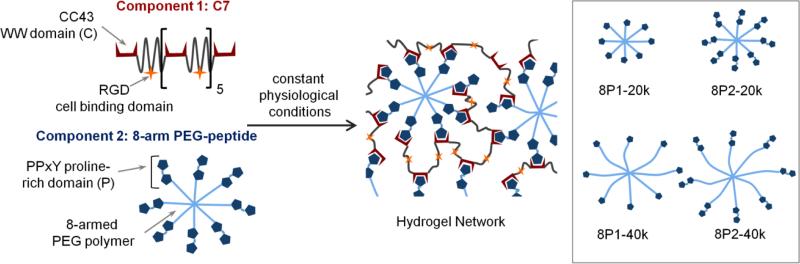
Fig. 1.
Schematic of MITCH-PEG hydrogel formation. Component 1 is a recombinant protein copolymer bearing CC43 WW domains (denoted as C) and RGD cell-binding domains. Component 2 is an 8-arm PEG-peptide conjugate bearing complementary proline-rich peptide domains (denoted as P). Simple mixing of the two components results in hydrogel network formation. Inset shows variants of the 8-arm PEG-peptide conjugate, created by varying domain repeat (P1 for one domain or P2 for two domains) and the PEG molecular weight (20 kD or 40 kD).