Figure 3.
Class M Sirtuins Lack Deacylase Activity
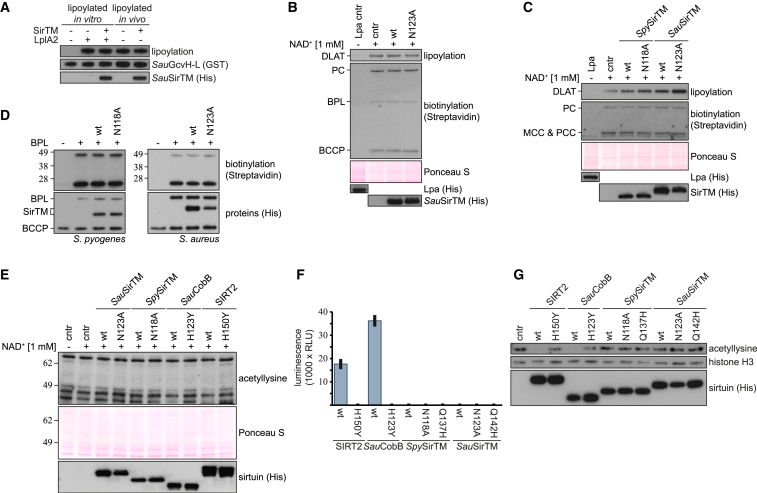
(A) Delipoylation assay performed with SauSirTM on in vitro and in vivo lipoylated SauGcvH-L. The in vitro lipoylation was carried out for 30 min prior to addition of SirTM and NAD+. Control samples with in vivo lipoylated SauGcvH-L were treated as “in vitro” samples, however, without addition of SauLplA2 and LA.
(B) Delipoylation and debiotinylation assay performed on S. aureus cell extracts. For lipoylation only, dihydrolipoamide S-acetyltransferase (DLAT) could be detected, whereas BCCP, biotin protein ligase (BPL), and pyruvate carboxylase (PC) could be identified as biotinylated. For assays on E. coli cell lysates, see Figure S3A.
(C) Delipoylation and debiotinylation assays were performed as in (B), but using human 293T cell extract. For lipoylation only DLAT could be detected, whereas PC, 3-methylcrotonyl-CoA carboxylase (MCC) and propionyl-CoA carboxylase (PCC) could be identified as biotinylated.
(D) Debiotinylation assay using recombinant, in vitro modified BCCP as substrate. Free biotin was removed from the initial biotinylation reaction by passing it twice over a desalting column.
(E) Deacetylation activity of SirTMs was tested on BL21(DE3)ΔCobB lysates. Human SIRT2 (isoform 2) and SauCobB were used as positive controls.
(F) Deacetylase activities of SauSirTM and SpySirTM against a p53-derived peptide were assessed using the SIRT-Glo assay (Promega). Data are background corrected means ± SD of triplicate measurements.
(G) Deacetylase activity of sirtuins (compare to F) was tested against penta-acetylated histone H3 (modified residues: K4, K9, K14, K18, and K23).