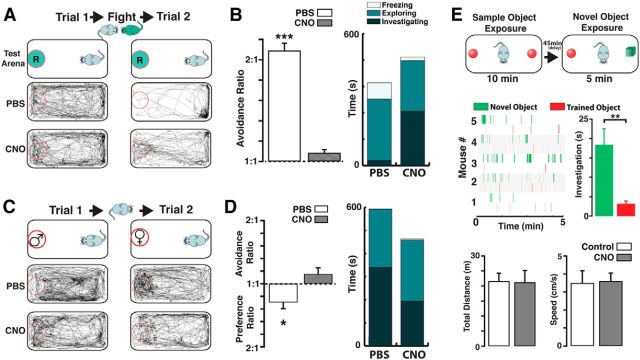
Figure 6.
Chemogenetic silencing of cholinergic neurons disrupts investigation of social odors. A, Top, Schematic illustration of the behavior paradigm used for the aggression-induced olfactory avoidance (see Materials and Methods). Before the aggressive encounter, a ChAT-hM4Di intruder (light blue) is placed in a neutral environment (Trial 1, 15 min), containing a dish with the soiled bedding from a resident (green circle marked “R”). Following the aggressive encounter, in which the intruder loses the fight, the same odor presentation is repeated (Trial 2, 15 min). Bottom, Movement trajectories during Trials 1 and 2, before the fight mice injected with PBS show no preference for a particular region of the neutral environment (left). After the fight, the mice spend most of the time avoiding the dish containing the resident's bedding (right). Following the fight, mice injected with CNO in the presence of the resident's bedding show no avoidance. B, Left, The avoidance ratio is significantly larger for the PBS-treated mice (white bar) compared with the CNO group (gray bar). Right, Stacked bar graph represents the average freezing (white), exploration (light green), and investigating (dark green) times, after fight (Trial 2) for PBS and CNO group. C, Top, Schematic illustration for the assessment of female odor preference (see Materials and Methods). During the first trial (Trial 1, 15 min), a ChAT-hM4Di male mouse is presented with a dish containing male-soiled bedding (red circle marked “♂”), whereas in the second trial (Trial 2, 15 min), the mouse is presented with a dish containing a female's soiled bedding (red circle marked “♀”). Bottom, Movement trajectories during Trials 1 and 2. In the presence of male bedding, mice injected with PBS navigate throughout the neutral environment indiscriminately (left). In the presence of female bedding, males spend significantly more time investigating the dish. In mice injected with CNO, the movement trajectories show decreased preference for a female's bedding. D, Left, The preference ratio is significant in the PBS-treated mice (white bar), whereas the CNO-treated mice show no preference, instead show a small but nonsignificant avoidance ratio (gray). Right, Stacked bar graph represents the average time spent by mice exhibiting freezing (white), exploration (light green), and investigation (dark green) behaviors during Trial 2 for the PBS and CNO groups. E, Top, Schematic illustration for the novel object recognition task. The trained object (red) consisted of a marble while the novel object was a cube (green, see Materials and Methods). Middle, Raster plots for the investigation events of the novel object in different ChAT-hM4Di mice injected with CNO. The mice spend a significant amount of time investigating the novel object. Bottom, The exploratory distance (left) and the average speed during the task is not affected by CNO. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.02; ***p < 0.01.