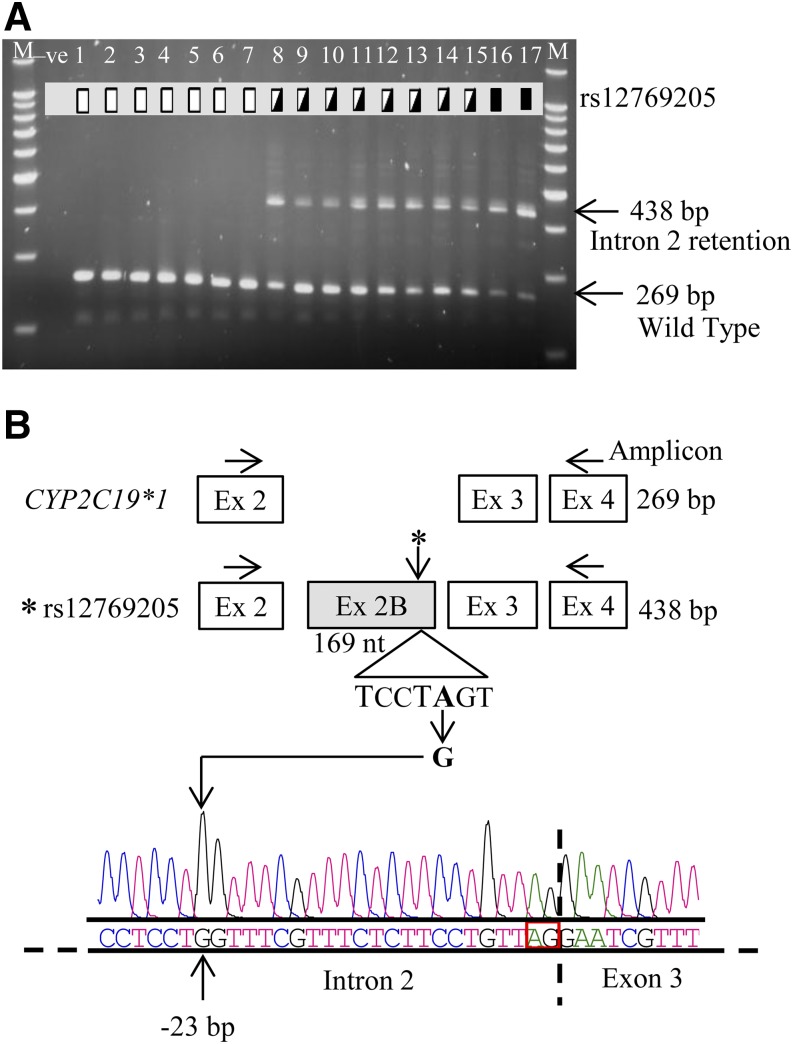
Fig. 1.
CYP2C19*35 (rs12769205) leads to aberrant intron 2 retention (exon 2B). (A) CYP2C19 cDNA was amplified from human liver cDNAs by PCR using primers in exons 2 and 4 and the wild-type product (269 bp) and alternatively spliced product (438 bp) analyzed on agarose gel. Homozygous wild-type (lanes 1–7 are CYP2C19*1/*1), rs12769205 heterozygous (lanes 8–15), and homozygous (lanes 16 and 17) variant genotypes are indicated by the open, half-filled, and filled boxes, respectively. Lanes marked M and –ve represent the 100 bp DNA ladder and a negative control, respectively. (B) The 438 bp fragment was excised from the gel and directly sequenced and the resulting electropherogram and nucleotide sequence are shown. The cartoon illustrates the amplification strategy, the insertion of exon 2B in samples with rs12769205, and the location of rs12769205 at the branch point adenine −23 nt upstream of the intron 2 splice acceptor site.