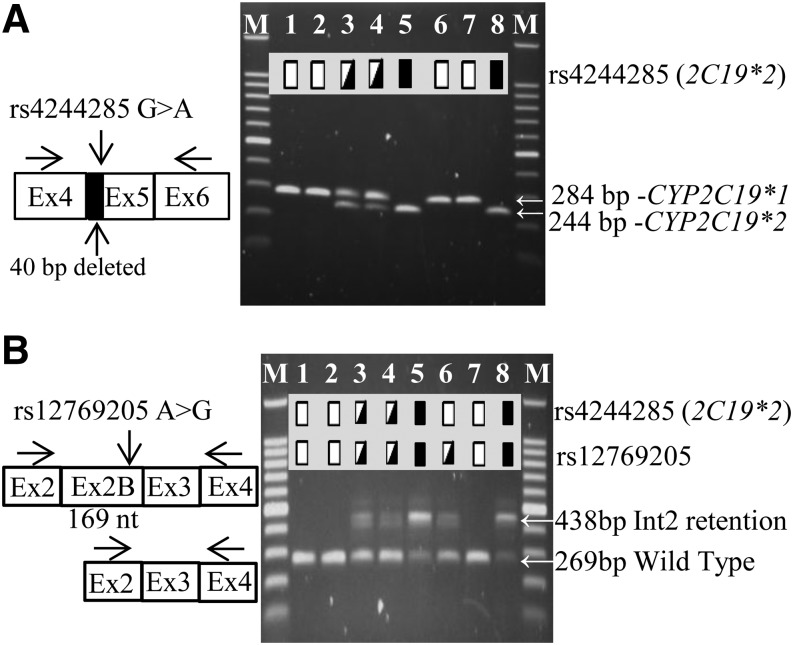
Fig. 3.
Effect of rs4244285 and rs12769205 on CYP2C19 splicing. (A) Eight liver samples were analyzed by PCR for (A) the CYP2C19 exon 5–40 bp deletion, caused by rs4244285, using primers in exons 4 and 6, and (B) the CYP2C19 exon 2B insertion, caused by rs12769205, using primers in exons 2 and 4 and the products analyzed on agarose gels. Arrows indicate the migration of the canonical and splice variant bands. Homozygous wild-type, heterozygous, and homozygous variant genotypes are indicated by the open, half-filled, and filled boxes, respectively. In (B), the smaller residual amount of the 269 bp wild-type mRNA is seen in rs12769205 heterozygous (lanes 3, 4, and 6) or homozygous (lanes 5 and 8) samples compared with samples 1, 2, and 7 homozygous for the CYP2C19*1/*1 genotype.