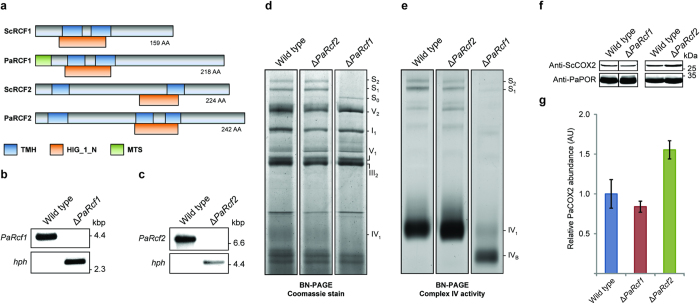
Figure 1. Deletion of PaRcf1 alters ETC composition.
(a) Comparison of S. cerevisiae and P. anserina RCF1 and RCF2 homologues. All proteins contain a hypoxia induced protein conserved region (HIG_1_N) domain and two or three predicted transmembrane helices (TMH). PaRCF1 additionally has a predicted mitochondrial targeting sequence (MTS). (b) Southern blot analysis of HindIII-digested genomic DNA (gDNA) from wild type and ΔPaRcf1. A PaRcf1-specific hybridization probe detects the 4217 bp PaRcf1-fragment only in wild-type gDNA. A 2659 bp fragment containing the hygromycin B phosphotransferase (hph) gene is detected only in gDNA of ΔPaRcf1. (c) Southern blot verification of ΔPaRcf2. The PaRcf2-fragment is 7153 bp and the hph-fragment 4667 bp in size. (d) Representative BN-PAGE analysis of mitochondrial protein extracts from the indicated strains. The I1III2IV0–2 (S0–2) supercomplexes, dimeric complexes III and V (III2 and V2) as well as monomeric complexes I, IV and V were visualized by Coomassie staining. (e) Representative complex IV ‘in-gel’ activity assay with mitochondrial protein extracts from the indicated strains. (f) Representative western blot analysis of mitochondrial protein extracts from wild type, ΔPaRcf1 and ΔPaRcf2. A ScCOX2-specific antibody was used to detect the ~29 kDa PaCOX2 subunit of complex IV. PaPORIN (PaPOR) was detected as a loading control. (g) Quantitative western blot analysis of mitochondrial protein extracts from wild type (n = 4), ΔPaRcf1 (n = 4) and ΔPaRcf2 (n = 4). The PaCOX2 abundance was normalized to that of PaPOR and the mean wild-type abundance was defined as 1. Data given in parentheses are mean PaCOX2 abundance ± s.e.m. in arbitrary units (AU).