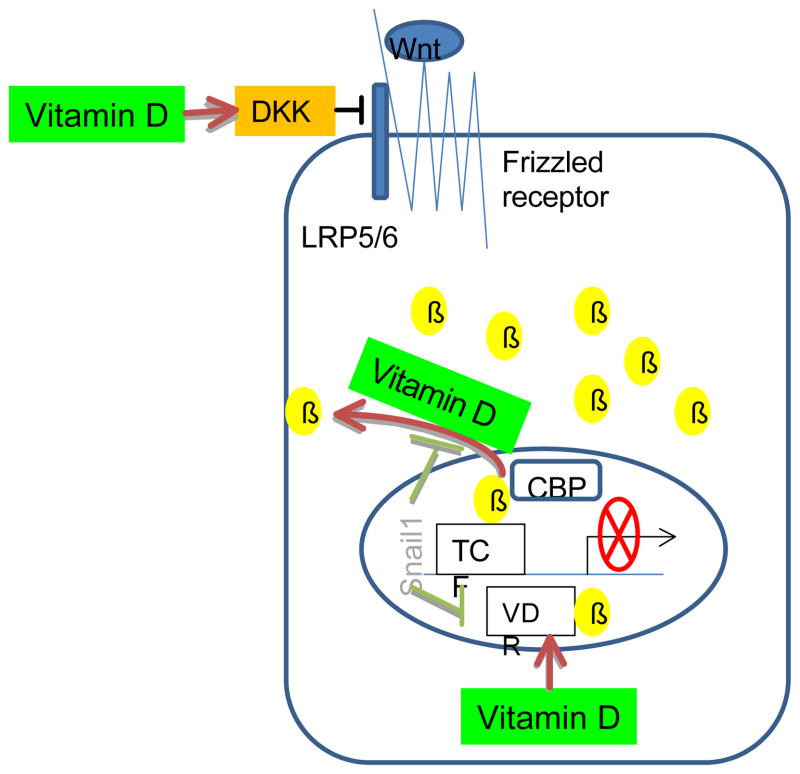
Figure 2.
Vitamin D suppresses the β-catenin-dependent canonical Wnt pathway in both stem and non-stem colon cancer cells. Vitamin D inhibits the aberrant activation of Wnt signals by stimulating Wnt repressor DKK, exporting β-catenin from nucleus to cytosol, and interefering with the TCF/ β-catenin mediated oncogene expression via the formation of VDR- β-catenin complex. The suppressive effects of vitamin D on the Wnt pathway may also arise from the indirect interference with Snail, a transcription factor that enhances Wnt signaling. DKK: dickkopf, β: β-catenin, CBP: CREB binding protein, TCF: T-cell factor, VDR: vitamin D receptor.