Figure 1.
Ras Inhibition Functions Downstream of IIS to Extend Lifespan
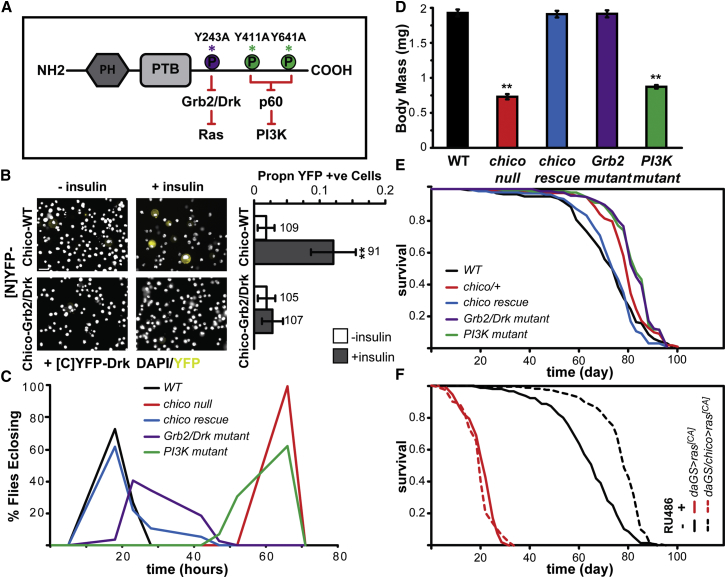
(A) Chico protein sequence with amino acid substitutions used to generate the Chico-Grb2/Drk- and Chico-PI3K-binding site mutants.
(B) BiFC in S2 cells co-expressing the indicated Chico constructs with the Drosophila Drk protein. Proportion of YFP-positive cells ± SE; n numbers are indicated above each bar; ∗∗p < 0.005 Chi-square test to no insulin control. Scale bar, 10 μm.
(C) Egg-to-adult development time of the indicated genotypes. See also Figure S1.
(D) Fresh weight of adult females of the indicated genotypes. Mean body mass (n = 10 for each genotype) ± SEM, Anova, p < 0.0001, ∗∗p < 0.05 t test (compared to WT).
(E) Survival of wild-type and chico/+ heterozygous females carrying the indicated chico genomic rescue constructs. chico/+ flies were long-lived compared to WT (p = 0.0006), which was rescued by the chico rescue construct (p = 0.58). Both the Grb2/Drk mutant and the PI3K mutant failed to rescue the longevity of chico/+ flies (compared to WT construct, p = 8.36 × 10−10 and p = 1.32 × 10−9, respectively). See Table S1A.
(F) Expression of constitutively active Ras blocks the beneficial effects of chico mutation on survival. daGS/chico > ras[CA] flies show increased lifespan compared to daGS > ras[CA] in the absence of RU486 (p = 3.07 × 10−18), but not in the presence of RU486 (p = 0.18). See Table S1B.