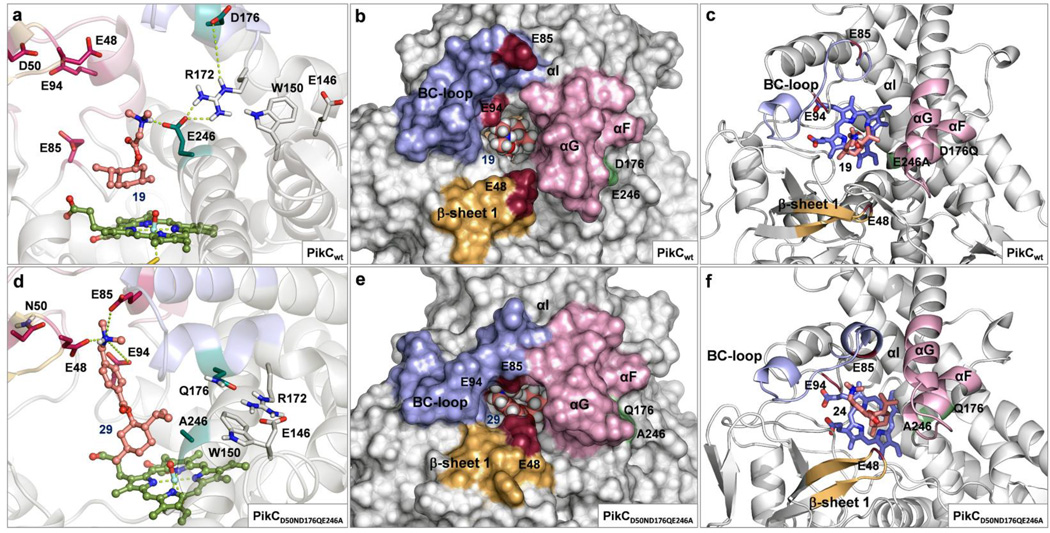
Figure 4. Substrate binding and tertiary structure of PikC variants observed in MD simulations.
(a) Improper binding of substrate (−)-21 to PikCwt showing detrimental interactions with E246, absence of contacts with E94, E85 or E48, and disruption of the hydrogen bond network in the R172/E146/W150 motif. (b and c) PikCwt in open conformation showing an open active site with widely spread binding residues (E94, E85 and E48). (d) Adequate binding of substrate (−)-26 to PikCD50ND176QE246A showing interactions with the all three binding residues simultaneously and the undistorted R172/E146/W150 motif. (e and f) PikCD50ND176QE246A in closed conformation showing a narrow active site channel and a tight arrangement of the binding residues.