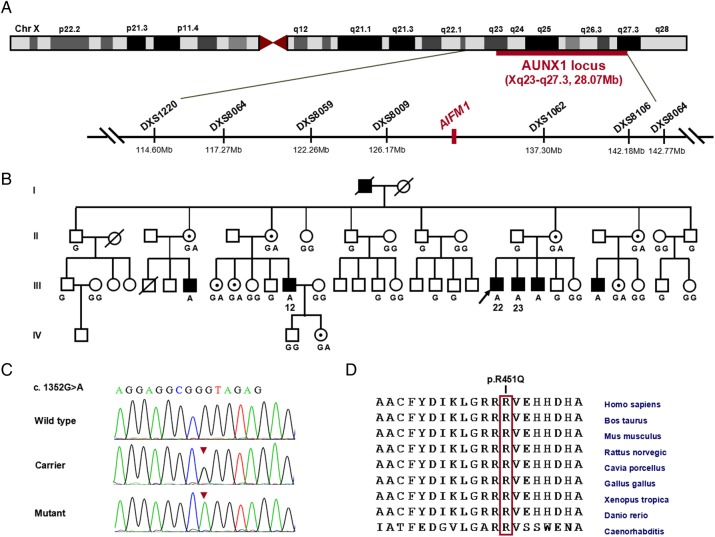
Figure 1.
Identification of the disease-causing AIFM1 mutation in the AUNX1 family segregating auditory and peripheral neuropathy. (A) Schematic genetic and physical map of the AUNX1 locus on chromosome Xq23-q27.3. The location of the AIFM1 gene is indicated (Mb, million bps). (B) The phenotype in AUNX1 family co-segregates with the c.1352G>A (p.R451Q) mutation in AIFM1. The genotypes at c.1352 for the family members are given: G or GG means hemi- or homozygous for the wild-type (WT) sequence, GA means c.1352G>A heterozygous, and A denotes the mutation in hemizygous form. Whole-exome sequencing was completed on subject III: 12. (C) Sequence chromatograms of exon 13 of AIFM1 show the c.1352G>A (p.R451Q) mutation (arrowhead) in affected males (hemizygote) and female carriers (heterozygote). A homozygous WT sequence is shown on the bottom. (D) Multiple sequence alignment depicts evolutionary conservation of amino acid residue Arg451 (red vertical bar) across human, bovine, mouse, chicken, Xenopus and zebrafish.