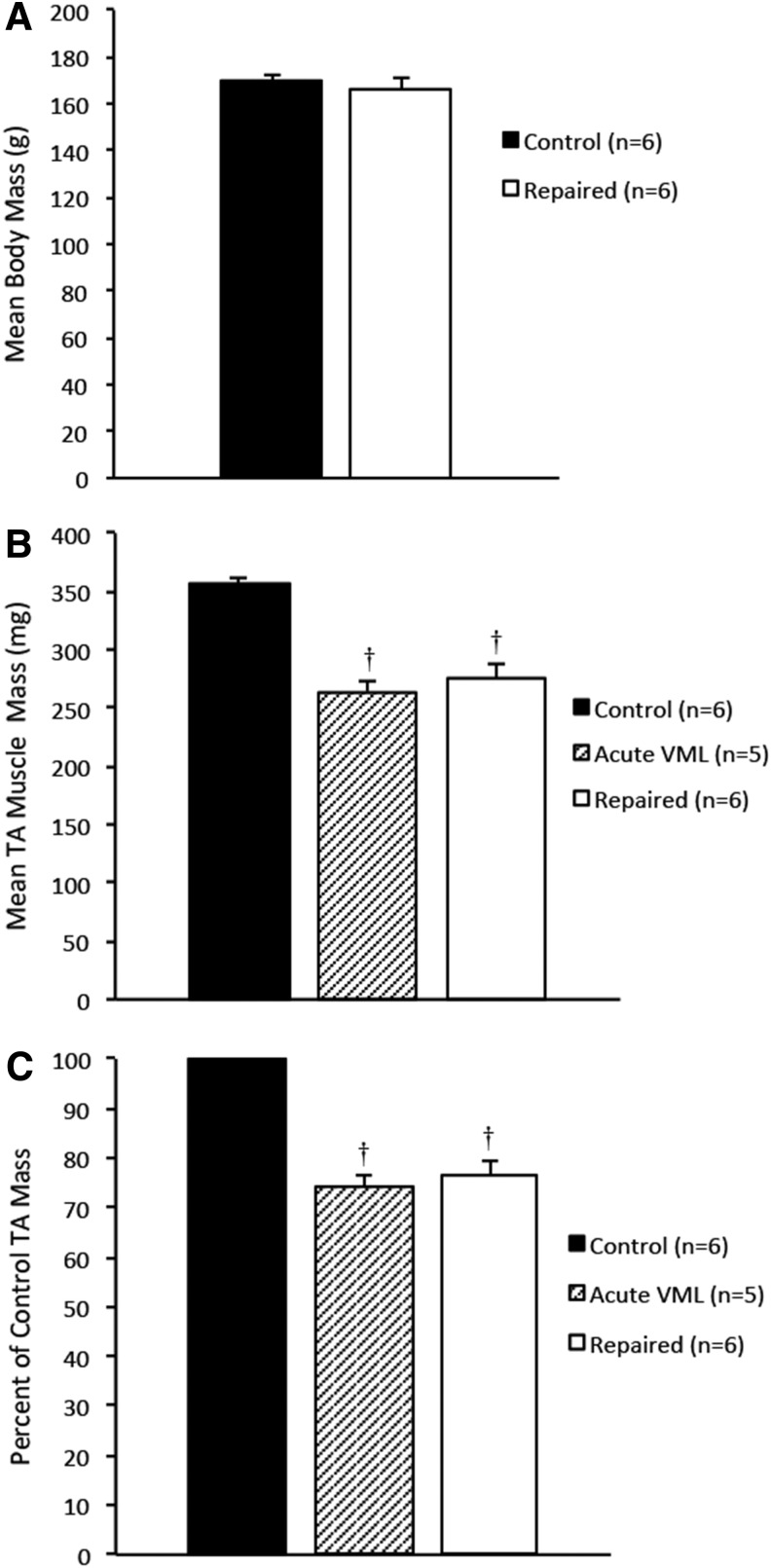
FIG. 2.
(A) A comparison of the average animal body masses in control, acute VML, and repaired VML groups shows no significant differences, indicating that direct comparisons of TA mass and force production can be drawn. (B) A comparison of TA masses shows a significant mass deficit in both the acute VML and the repaired TA groups in comparison to the control group (p<0.0001 and p=0.0002, respectively). The difference in average TA mass between these groups was not significant, indicating that the SMUs did not appreciably restore muscle volume to the repaired TAs in 28 days. (C) Normalized to the average control TA mass, the damage to the acute VML TAs constituted a 26%±2.1% mass deficit and the repaired TAs were found to have a 22%±2.8% mass deficit. Error bars indicate standard error. †Statistical difference from control group.