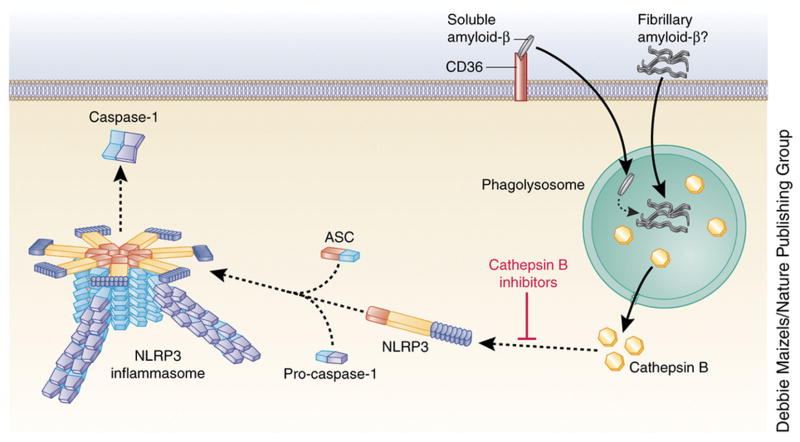
Figure 3. Mechanisms of NLRP3 inflammasome action in Alzheimer’s disease.
In Alzheimer’s disease, CD36 mediates the internalization of soluble amyloid-β and its intracellular conversion to fibrillary amyloid-β. This leads to disruption of the phagolysosome and activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome due to cathepsin B release. However, this does not exclude the possibility that phagocytosis of extracellular fibrillary amyloid-β also activates the NLRP3 inflammasome. Cathepsin B inhibition prevents amyloid-β–induced NLRP3 activation.