Fig 1. Phylogenetic analysis of thiG, ∆thiG construction, and its molecular confirmation.
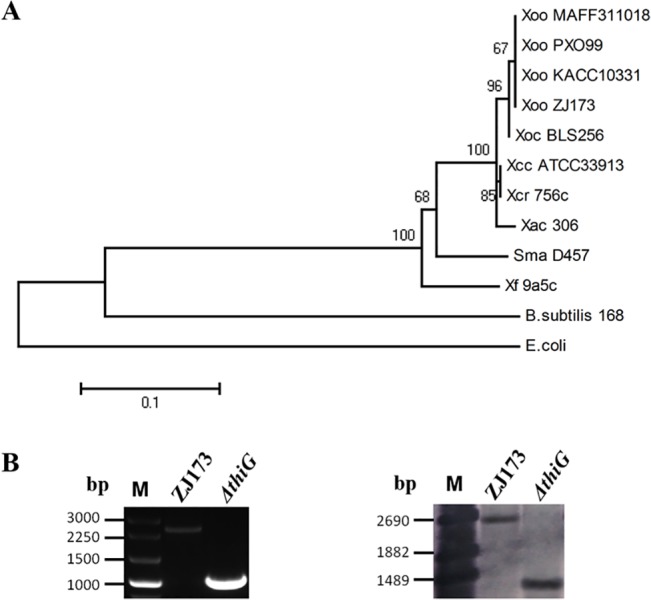
(A) Phylogenetic analysis of thiG within the family Xanthomonadaceae and model bacterial strains Abbreviations: Xoo, Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae; Xoc, Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzicola; Xac, Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. citri; Xcc, Xanthomonas. campestris pv. campestris; Xcr, Xanthomonas. campestris pv. Raphani; Sma, Stenotrophomonas maltophilia; Xf, Xylella fastidiosa; E. coli, Escherichia coli; B. subtilis, Bacillus subtilis. The scale bar (0.1) means 10% sequence divergence. Bootstrap values are a value for the significance of the branches. (B) PCR confirmation and Southern blot analysis of thiG mutant. The deletion of the ORF for thiG resulted in the amplification of a 1000 bp fragment of the deletion mutants. M: mark. The primers used to amplify the probe for the Southern blot are listed in Table 1. DNA fragments of approximately 1400 bp were detected in the thiG deletion mutant, whereas the corresponding fragments detected in the wide-type strain ZJ173 were 2500bp.
