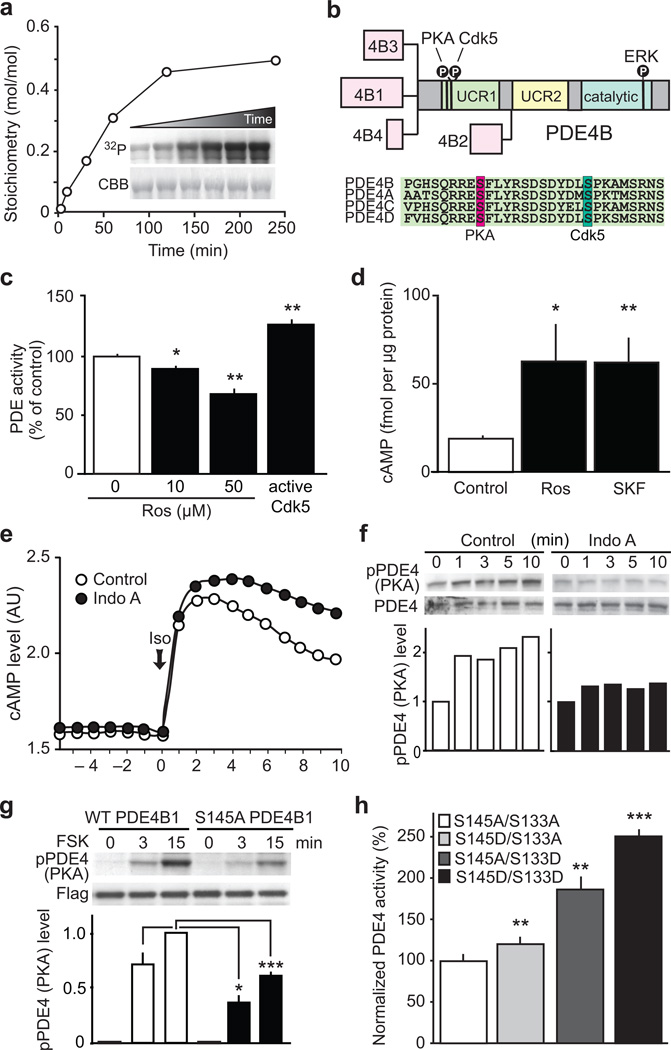
Figure 1.
Cdk5 regulates cAMP signaling via phosphorylation of PDE4. (a) Cdk5 phosphorylates PDE4B1 in vitro. Inset: 32P radiographic (32P) and Coomassie stained (CBB) gels of reactions. (b) PDE4B isoforms schematic and amino acid sequence alignment of PDE4 family members. (c) Cdk5 inhibition with roscovitine (Ros) attenuates PDE activity, whereas enzymatically active Cdk5 increases PDE activity in striatal lysates (n = 4 slices; Ros 10 µM: *P = 0.011; Ros 50 µM: **P = 0.0037; Cdk5/p25: *P = 0.006). (d) Cdk5 inhibition with Ros and D1 receptor activation using SKF81297 (SKF) increase cAMP to similar levels in striatal slices (Control and Ros n = 3 slices; SKF n = 4 slices; Ros: *P = 0.0216; SKF: **P = 0.0030). (e) Cdk5 inhibition with Indolinone A (Indo A, 10 µM) reduces cAMP hydrolysis after stimulation with isoproterenol (Iso; 30 nM). (f) PKA-dependent activation of PDE4 is attenuated by Indo A. (g) Mutation of the Cdk5 site, Ser145, to Ala in PDE4B1 (S145A PDE4B1) reduced PKA-mediated PDE4 phosphorylation after forskolin (FSK; 10 µM) treatment in PC12 cells (n = 8 reactions; WT vs S145A at 3 min: *P = 0.0241; WT vs S145A at 15 min: ***P < 0.0001). (h) Mutational analysis of the relative contributions of the Cdk5- and PKA-dependent phosphorylation sites on PDE4 to PDE activity (n = 4 reactions; S145D vs S133A **P = 0.0082; S145A vs S133D **P = 0.0019; S145D vs S133D ***P < 0.0001). Whole immunoblot images are presented in Supplementary Fig. 13. All data shown are means ± s.e.m., *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.