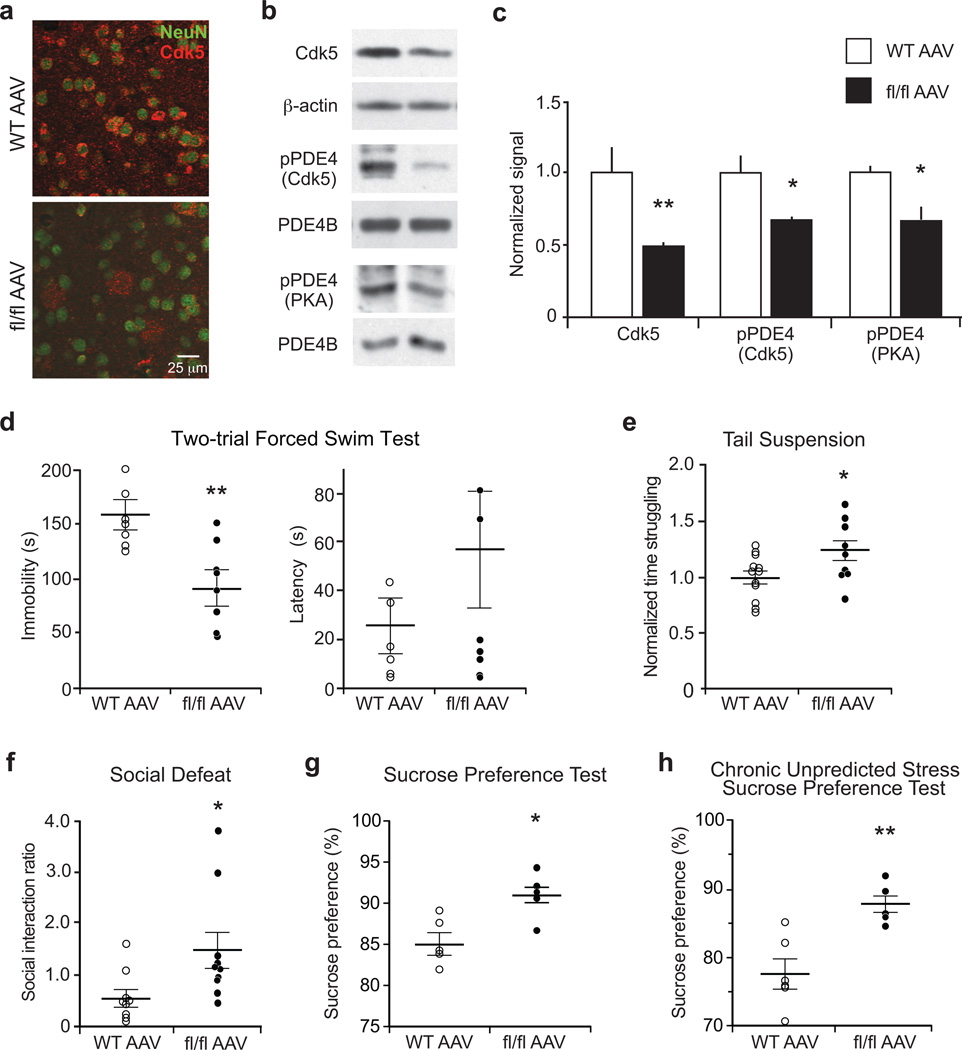
Figure 3.
Virus-mediated Cdk5 knockout in ventral striatum reduces PDE4 phosphorylation and alters stress-induced behaviors. (a) Immunostain showing virus-mediated Cdk5 knockout in NAc neurons of homozygous floxed Cdk5 (fl/fl AAV) mice. (b,c) Reduced Cdk5 expression and PDE4 phosphorylation at the Cdk5 and PKA sites in ventral striatum of fl/fl AAV mice (WT n = 4; fl/fl AAV n = 5; Cdk5: **P = 0.0037; pPDE4 (Cdk5): *P = 0.0164; pPDE4 (PKA): *P = 0.0176;). (d–h) Effect of AAV2-cre-mediated Cdk5 loss in ventral striatum on behavioral responses in paradigms of acute and chronic stress. The fl/fl AAV mice showed reduced immobility time in FST (WT n = 6; fl/fl AAV n = 7; **P = 0.0065) (d), increased time struggling in TST (WT n = 12; fl/fl AAV n = 9; *P = 0.04225) (e), increased social interaction ratio in SD (WT n = 9; fl/fl AAV n = 10; *P = 0.0314) (f), and elevated sucrose preference in SPT (n = 5 mice; *P = 0.0116) (g), as well as in the CUS paradigm (WT n = 6; fl/fl AAV n = 5; **P = 0.0027) (h). Whole immunoblot images are presented in Supplementary Fig. 13. All data shown are means ± s.e.m., *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.