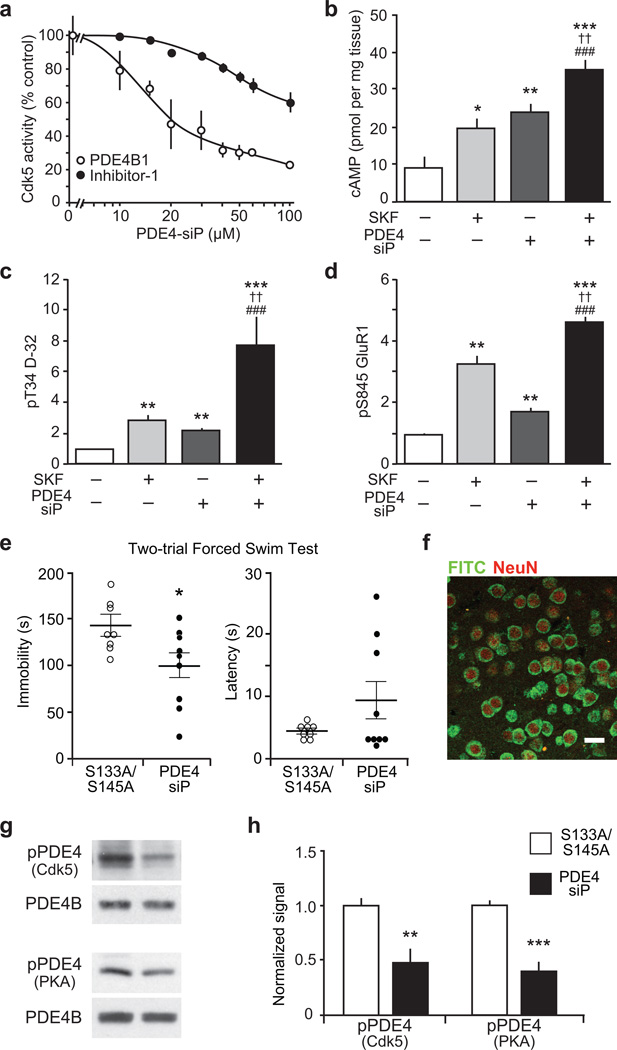
Figure 4.
Development of a small interfering peptide (siP) that raises cAMP levels, increases PKA activity and reduces immobility time in the FST. (a) PDE4-siP inhibits phosphorylation of PDE4B1 by Cdk5, more effectively than inhibitor-1 (I-1) phosphorylation by Cdk5. (b–d) Effects of the D1 dopamine receptor agonist SKF81297 (SKF), PDE4-siP, or both on cAMP (b), pT34 D-32 (c) and pS845 GluR1 (d) are shown. ††P < 0.01 compared to SKF81297, ##P < 0.01 compared to PDE4 peptide, ###P < 0.005 compared to PDE4 peptide; one-way ANOVA and Newman-Keuls test, (n = 4–6 slices). (e) FST immobility time is reduced in mice infused with PDE4-siP into ventral striatum as compared to mice treated with peptide containing serine to alanine substitutions (S133A/S145A) (S133A/S145A n = 8; PDE4-siP n = 9; Immobility: *P = 0.0285; Latency: P = 0.1498). (f) Immunostain of FITC-tagged peptide infused into the ventral striatum; scale bar = 25 µm. (g,h) PDE4 phosphorylation at the Cdk5 and PKA sites is reduced in mice with intra-striatal infusion of PDE4-siP (S133A/S145A n = 5; PDE4-siP n = 6; pPDE4 (Cdk5): **P = 0.0071; pPDE4 (PKA): **P = 0.0002). Whole immunoblot images are presented in Supplementary Fig. 13. All data shown are means ± s.e.m., *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.