Figure 3.5.
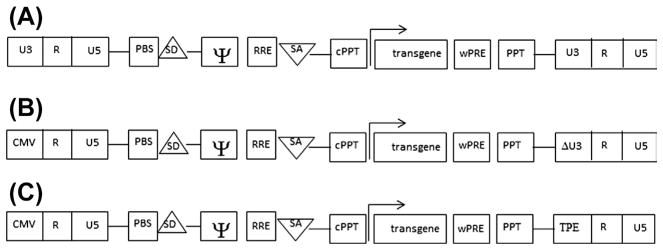
Development of the expression (transgene) cassette. (A) First generation contains wild-typed 5′- and 3′-LTRs, primer-binding site (PBS), splice donor (SD), and splice acceptor (SA), central polypurine tract (cPPT) and polypurine tract (PPT), Rev response element (RRE), woodchuck hepatitis virus posttranscriptional regulatory element (wPRE), and the retroviral vector packaging element, psi (Y) signal. Expression of a transgene is driven from the promoter-of-choice shown by the arrows. (B) SIN vector is devoid of the parental enhancer/promoter sequences, located at the U3′ of the 3 ′-LTR (deletion is shown); thus, lacking the ability to transcribe full-length mRNA. CMV promoter incorporated in the 5′-LTR employed to generate full-length mRNA. (C) Inducible expression cassette drives from the tetracycline response element (TRE) incorporated in the U3 region of the 3′-LTR. This cassette named a conditional SIN cassette, expressing the genome in the presence of the ttA. SIN, self-inactivating; LTR, long terminal repeat; CMV, cytomegalovirus.
