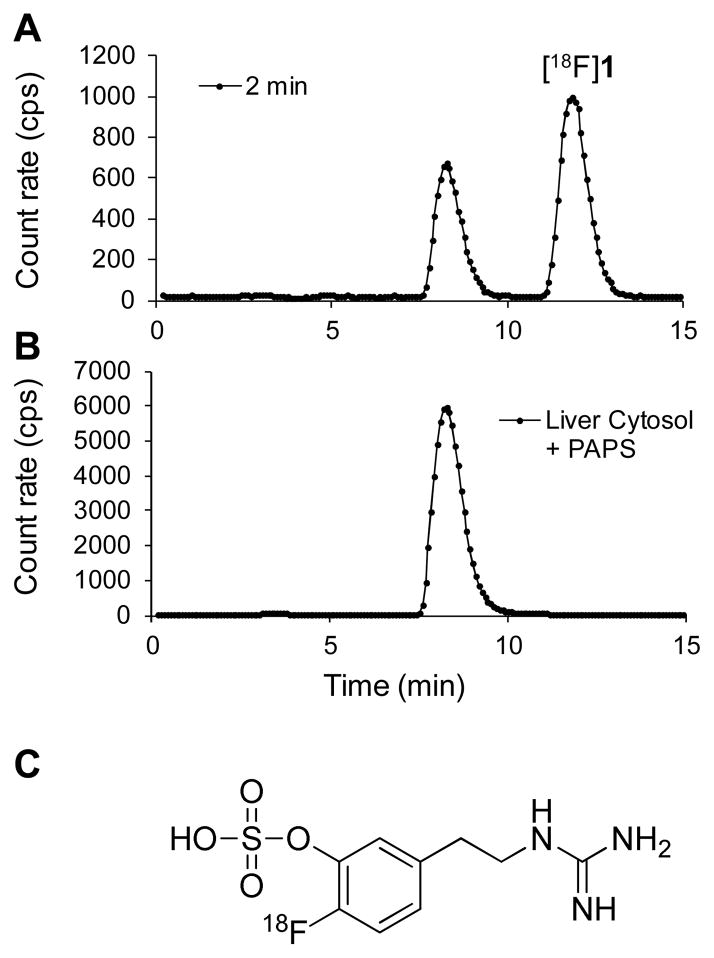
Figure 4.
Radiodetection data from reverse-phase HPLC analysis of [18F]1 and its radiolabeled metabolites. The top curve (A) is data for a plasma sample taken from a rhesus macaque monkey 2 min after administration of [18F]1, which shows a polar metabolite at retention time Rt ~ 8.2 min. The bottom curve (B) is data from an in vitro incubation of [18F]1 with a monkey liver cystosol fraction plus the cofactor for sulfur conjugation, 3′-phospho-adenosine-5′-phosphosulfate (PAPS), at 37 °C for 20 min. The retention time of the sulfur conjugate of [18F]1 is the same as that of the main metabolite observed in the monkey study (top curve), strongly suggesting that sulfur conjugation is the primary metabolic pathway for [18F]1 in rhesus macaques. The structure of the sulfur conjugate of [18F]1 is shown (C).